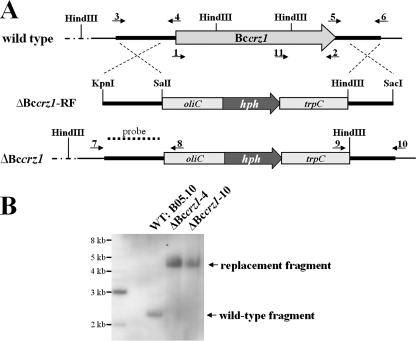
FIG. 3.
Gene replacement of Bccrz1. (A) Physical maps of Bccrz1, the gene replacement fragment ΔBccrz1-RF, and the gene locus of a Bccrz1 knockout mutant showing the Bccrz1 open reading frame (gray arrow), the components of the hygromycin resistance cassette (gray boxes), and the flanking regions of Bccrz1 (heavy lines). The small arrows indicate the positions of primers used for cloning the full-length cDNA for yeast complementation (primers 1 and 2), the replacement vector (primers 3 to 6), and the diagnostic PCR analysis of the transformants (primers 7 to 11) (see Materials and Methods). (B) For Southern blot analysis, the genomic DNAs of the wild type (WT) and the mutants were digested with HindIII, blotted, and hybridized to the 5′ flank (dotted line in panel A) of the replacement vector pΔbccrz1. In both mutants, the wild-type fragment, with a size of 2.2 kb, was replaced by a 4.5-kb fragment, resulting from the loss of HindIII restriction sites within the Bccrz1 gene.