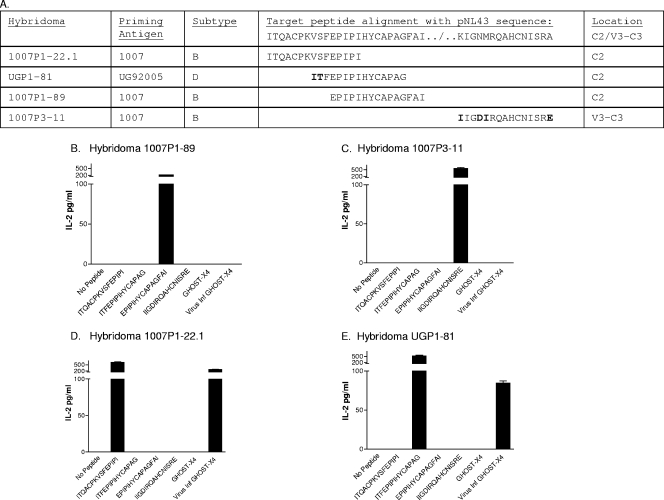
FIG. 1.
The peptide sequence within HIV-1 does not ensure T-cell activation. (A) Hybridomas are listed with the names, subtypes, and target sequences of the priming antigens. The target sequences are aligned with sequences from HIV-1NL4-3. Residue differences are indicated in bold. (B to E) The IL-2 responses of hybridomas 1007P1-89, 1007P3-11, 1007P1-22.1, and UGP1-81 toward peptides (10 μM) or GHOST cells (105 cells either infected with HIV-1NL4-3 or uninfected) were measured. The HIV-1NL4-3 used for GHOST cell infections was prepared by first purifying DNA (with a Qiagen maxiprep kit) from bacteria carrying the pNL4-3 infectious clone (originally derived from HIV-1IIIB; National Institutes of Health AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Repository [catalogue no. 114 for pNL4-3]). DNA was then used to transfect 293 T cells in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium-l-glutamine (without fetal calf serum) with Lipofectamine plus reagent (Invitrogen) as recommended by the manufacturer. After a 3-h incubation at 37°C and 5% CO2, cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium plus 20% fetal calf serum for 2 days. The virus from 293 T-cell supernatants was expanded on GHOST-X4 cells (an osteosarcoma cell line; AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Repository) in R10 medium (RPMI 1640, 10% fetal calf serum, glutamine, and antibiotics) for 3 days and stored frozen.