Figure 3. Inactivation of Sd blocks tissue overgrowth induced by Yki or Hpo pathway mutations.
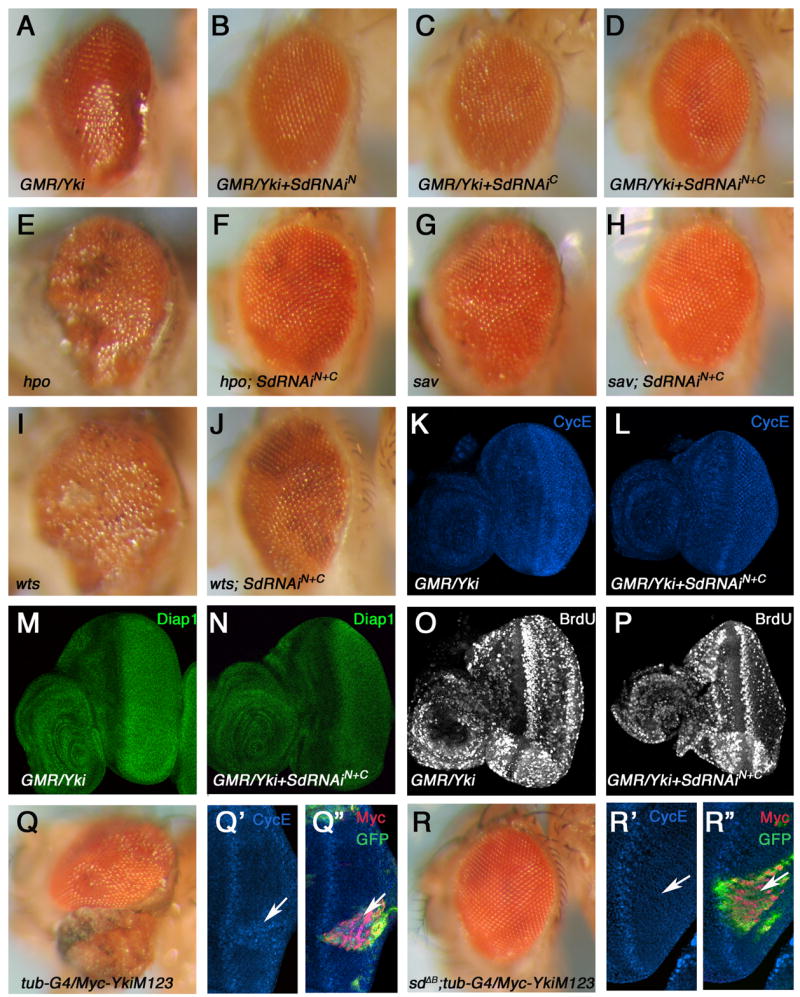
(A–D) Adult eyes of GMR-Gal4 UAS-Yki (A), GMR-Gal4 UAS-Yki; UAS-Sd-RNAiN (B), GMR-Gal4 UAS-Yki; UAS-Sd-RNAiC (C), and GMR-Gal4 UAS-Yki; UAS-Sd-RNAiN +UAS-Sd-RNAiC (D). (E–J) Adult eyes containing hpo (E), sav (G), or, wts (I) mutant clones or corresponding mutant clones that express UAS-SdRNAiN and UAS-SdRNAiC (F, H, J). (K–P) cycE (K–L) and diap1 (M–N) expression, and BrdU incorporation (O–P) in eye discs expressing Yki (K, M, O) or Yki plus Sd RNAi transgenes (L, N, P) with GMR-Gal4. (Q–Q″) Adult eye (Q) or eye disc (Q′, Q″) with YkiM123 expressing clones. YkiM123 expressing cells were recognized by Myc (red) and GFP (green) staining in discs (Q″). (R–R″) Adult eye (R) or eye disc (R′, R″) with sd B clones expressing YkiM123. sd B mutant cells expressing YkiM123 were labeled by both Myc and GFP expression (R″).
