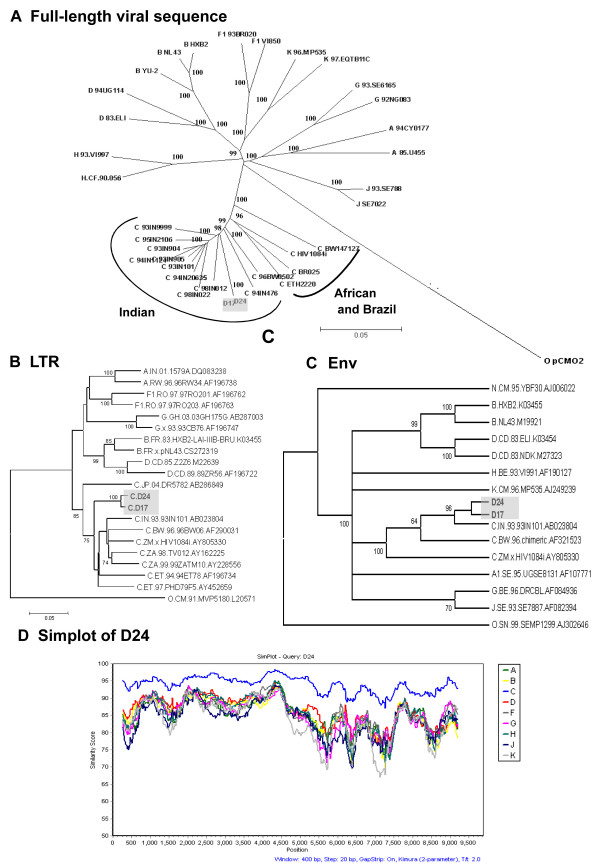
Figure 3.
Sequence analysis of the molecular clones D17 and D24. (A) Phylogenetic relationship of the molecular clones. Full-length sequences of D17 and D24 (shaded) were compared with representative HIV-1 sequences of subtypes A, B, C, D, F, G, H, J and K. subtype C sequences from India were also included in the analysis. A neighbor-joining tree was constructed on the basis of the hidden Markov model nucleotide alignment of full-length HIV-1 genomes. Subtype O pCMO2 sequence was used as the outgroup. Horizontal branch lengths are drawn to scale with the scale bar representing 0.05 nucleotide substitution per site whereas the vertical separation is only for clarification. Figures along the branches indicate the bootstrap values that support branching, out of a total of 1,000 resamplings. The reference sequences for different HIV-1 groups and subtypes were obtained from the HIV sequence database[97]. Phylogenetic trees of D17 and D24 based on the LTR (B) and the Env (C) sequences. Phylogenetic trees were constructed from full-length LTR and Env nucleotide sequences by using the neighbor-joining method. Major subtypes of HIV-1 group M were used as reference sequences. Trees were rooted by using subtype O strains as outgroups. Accession numbers for each of the references sequences used in the above plots could be obtained by using the name of the viral strain shown (D) Plot of similarity of D24 to a set of reference subtype genomes. Analysis was performed with the SimPlot program using a window size of 400 nucleotides and a step size of 20 nucleotides. Positions containing gaps were excluded from the comparison. The x-axis indicates the nucleotide positions along the sequence alignment. The y-axis denotes the distance between compared sequences plotted at the midpoint of the 400-nucleotide window. Identical results were obtained with the clone D17 (data not presented).