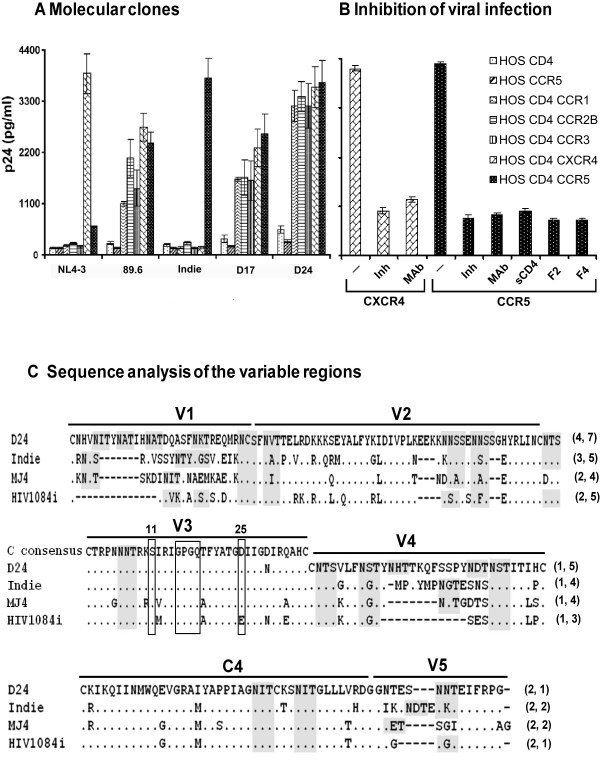
Figure 6.
Coreceptor phenotyping of the viral molecular clones. (A) Profile of coreceptor use in HOS cell lines. HOS cell lines expressing CD4 and one of the several coreceptors including CCR1, CCR2B, CCR3, CXCR4 and CCR5 or CD4 alone or CCR5 alone were tested for viral infectivity. These cell lines were infected overnight with one of the viral molecular clones (89.6, NL4-3, Indie-C1, D17 and D24), residual virus was washed off and the cells were incubated up to 14 days. Secretion of p24 into the medium was monitored every third day using a commercial kit and data for day-7 are presented here. Data are representative of at least four independent experiments and presented as mean quantity of p24 released in triplicate wells ± 1 SD. Identical results were obtained at other time points. (B) Inhibition of the viral infection using receptor-specific inhibitors. Target cells, HOSCD4CXCR4 and HOSCD4CCR5, were infected with the viruses in the absence or presence of one of the inhibitors (Inh) at appropriate concentration. CXCR4 inhibitor bicyclam JM-2987 at 60 nM, CCR5 inhibitor TAK-779 at 20 μM, soluble CD4 (sCD4) at 1 μg/ml and two different anti-human CD4 monoclonal antibodies F2 and F4 at 0.5 μg/ml were used. In a similar fashion, we used coreceptor-specific monoclonal antibody pools (Mab), 0.5 μg of each antibody, to block viral infection, antibodies # 1012 and # 1009 for CXCR4 (Pro-science, Poway, CA) and antibodies #182 (R&D systems) and #624085 (BD Biosciences) for CCR5. The residual virus and the inhibitors were removed after overnight incubation and the p24 production was monitored in the culture supernatants. Data for only D24 virus on day-7 post-infection are presented here and identical results were obtained at other time points and with other viruses. (C) Amino acid sequence comparison of the gp120 extra-cellular variable loops and the C4 domain. The amino acid sequences of D24 env loops are aligned with those of the three available subtype C infectious molecular clones. Dots indicate sequence homology and dashes gaps. For the V3 loop, subtype C consensus sequence is presented at the top and the positions 11 and 25 and the 'GPGQ' motif have been highlighted using open boxes. Putative N-linked glycosylation sites have been highlighted using shaded boxes. Figures in the parentheses indicate the number of potential glycans in respective loops. Viral clone D17 is not shown here as the amino acid sequences of D17 and D24 in gp120 differ from each other at only one position.