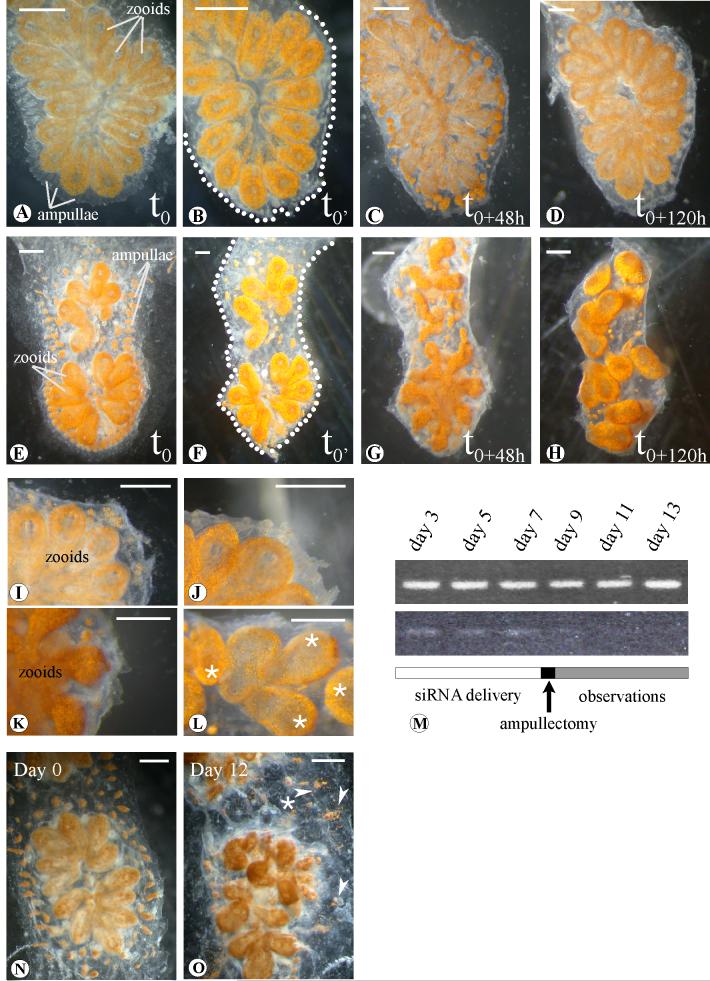
Figure 5.
Morphological analysis of the effects induced by BsVEGFR siRNA treatment. (A-D), Botryllus schlosseri systems injected with Botryllus buffer only; (E-H), systems of the same genotype treated with BsVEGFR siRNA (in Botryllus buffer). (B) and (F) samples immediately after the complete ablation of ampullae and marginal vessel (t0’). (C), (G) (D) and (H), snapshots after 48 hours (t0+48h) and 120 hours (t0+120h) respectively: treated samples do not show vascular regrowth in comparison to the controls, after the takeover (C, G) the treated samples bud chaotically and loose the characteristic star-shaped form.Close-up view of untreated samples 48 hours (I) and a week (J) after the complete ampullaectomy. (K) and (L), magnification of marginal tunic in silenced systems after 48 and 120 hours ampullae surgical ablation (oral siphons indicated by asterisks). (M), RT-PCR at different days after the first siRNA injection: BsVEGFR siRNAs treated samples show reduction of the transcript while controls (top), injected with Botryllus buffer, maintain appreciatively the same transcript levels. Detail of a colony before treatment with BsVEGFR siRNA. Day 0 (N) and 12 days (O) after daily injections and/or soaking. Arrowheads show exploded ampullae and vessels leaking pigmented cells in the tunic. Dots underline the edge of the cut. Scale bar 1mm.