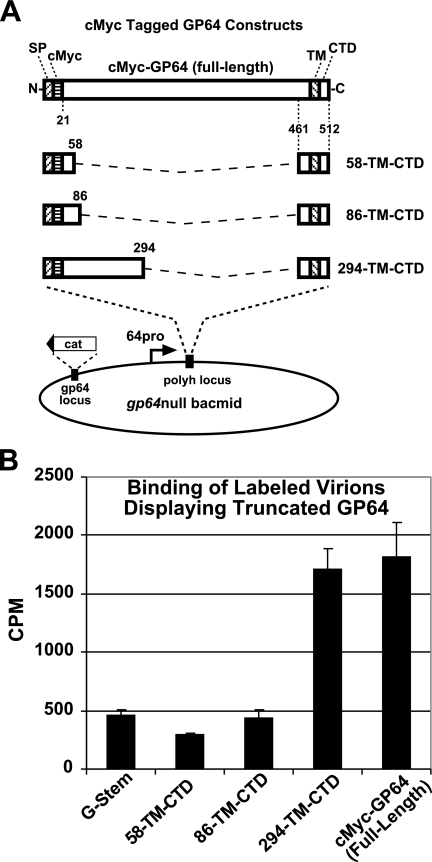
FIG. 4.
Analysis of Sf9 cell binding by gp64null AcMNPV BV displaying truncated forms of GP64. (A) Strategy for construction of GP64 proteins with C-terminal ectodomain deletions and insertion into a gp64null bacmid. Each construct contains a C-terminal GP64-stem domain and various portions of the GP64 ectodomain, as illustrated. The GP64-stem domain consists of amino acids 461 to 512 from the C terminus of the AcMNPV GP64 protein (22 residues from the predicted GP64 ectodomain, 23 residues from the predicted GP64 TM domain, and the 7-residue CTD). Various portions of the GP64 ectodomain were fused to the GP64-stem such that in the mature protein, the protein construct contained a c-Myc epitope tag and 38 (residues 21 to 58), 66 (residues 21 to 86), 138 (residues 21 to 158), or 274 (residues 21 to 294) amino acids from the N terminus of the GP64 ectodomain. (B) Analysis of virion binding to Sf9 cells. Labeled virions displaying truncated GP64 proteins were examined for binding to Sf9 cells. Production of virions displaying truncated GP64 proteins was augmented by coexpression of a VSV G-stem construct (vAc/G-stem) that mediates virion budding (54). Progeny virions were labeled with [35S]methionine, purified, and bound to Sf9 cells at 4°C. Labeled virus bound to Sf9 cells was quantified, and cpm values are indicated. Each bar represents the average value from three independent experiments with three replicates.