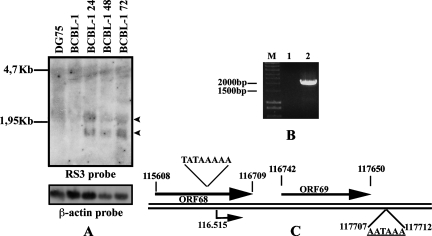
FIG. 2.
ORF69 transcription analysis in BCBL-1 cells. (A) Kinetics of ORF69 expression upon chemical induction in BCBL-1 cell line. Cells were untreated or induced with TPA for 24, 48, or 72 h; total RNA was prepared at the times indicated, and 20 mg was analyzed by Northern blotting. As a negative control, RNA from DG75 treated with TPA for 72 h was loaded. The filter was hybridized with an oligonucleotide specific for ORF69 (RS3 probe) and subsequently with a β-actin probe. The two specific ORF69 transcripts are shown with arrowheads. (B) ORF68-ORF69 bicistronic transcript. Reverse transcription was performed on total RNA from BCBL-1 cells treated with TPA for 48 h by using oligo(dT), and PCR was carried out with primers I and II. Nucleotide sequences of primers I and II are described in Materials and Methods. Lanes: M, marker; 1, PCR without reverse transcription; 2, RT-PCR. (C) 5′-3′ RACE analysis of ORF69 transcript. Schematic drawing of the location of ORF69 in the KSHV genome. Numbers correspond to nucleotide positions, and arrows indicate the direction ORF68 and ORF69. The ORF69 transcription start is at position 116515. TATAAAAA is the putative TATA box. AATAAA is the polyadenylation recognition sequence.