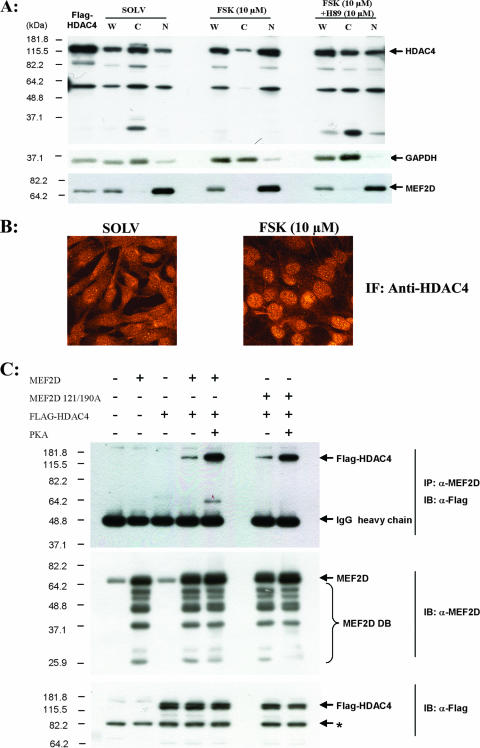
FIG. 9.
PKA increases HDAC4 nuclear localization and association with MEF2D. (A) C2C12 myoblasts were cultured in low-mitogen medium for 3 h and then treated with either solvent (dimethyl sulfoxide [DMSO]), FSK (10 μM), or H89 (PKA inhibitor [10 μM]) for 6 h prior to being harvested. Whole-cell (W), cytoplasmic (C), and nuclear (N) extracts were obtained as described in Materials and Methods. Equal amounts of total protein (10 μg) were loaded for all samples. Western blotting was performed using anti-HDAC4 to check the HDAC4 localization. Immunoblotting using anti-glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and anti-MEF2D was used as cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction markers, respectively. (B) C2C12 myoblasts were cultured in low-mitogen medium for 3 h and then treated with either solvent (DMSO) or FSK (10 μM) for 6 h prior to 4% formaldehyde fixation. Indirect immunocytochemistry was performed by using anti-HDAC4. The images were captured using a Fluoview 300 (Olympus) confocal microscope. (C) Cos7 cells were transfected with the indicated combinations of pcDNA3, Flag-HDAC4, pcDNA3-MEF2D, pcDNA3-MEF2D S121/190A, and pFC-PKA. Coimmunoprecipitation was performed using anti-MEF2D and immunoblotted with anti-MEF2D or anti-Flag (for HDAC4 detection). (Top) PKA treatment resulted in qualitatively more Flag-HDAC4 association with MEF2D and MEF2D S121/190A. (Middle and bottom) Immunoblots of cell lysates showing the expression of MEF2D and Flag-HDAC4 used in the coimmunoprecipitation experiment.