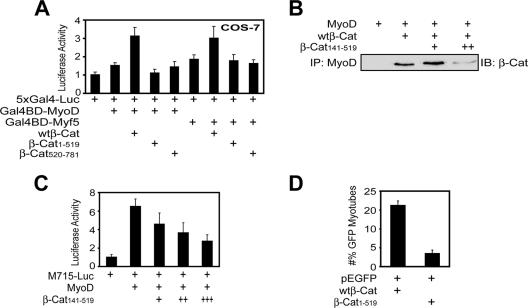
FIG. 6.
β-Cat is necessary for MRFs transcriptional activity. (A) The requirement of the C-terminal transactivation domain of β-Cat for MyoD or Myf5 transcriptional activity. Luciferase activities in transfected COS-7 cells were assayed as in Materials and Methods. (B) Disruption of the β-Cat-MyoD interaction by β-Cat141-519. Recombinant His-MyoD, β-Cat141-519, and wild-type β-Cat (wtβ-Cat) were produced and purified from bacteria. His-MyoD was incubated with wtβ-Cat without or with increasing concentrations of β-Cat141-519. Bound β-Cat1-781 was isolated by immunoprecipitation (IP) and visualized by immunoblotting (IB) with the monoclonal antibody that recognizes only the C-terminal region of β-Cat. ++ indicates doubled amounts of β-Cat141-519. (C) β-Cat141-519 inhibited MyoD transcriptional activity. C2C12 myoblasts were transfected with M715-Luc and pRL-TK without or with MyoD and increasing amounts (+, ++, and +++) of β-Cat141-519. Luciferase assays were performed as in Materials and Methods. (D) The transactivation domain of β-Cat was necessary for C2C12 differentiation. C2C12 myoblasts were transfected with pEGFP-C1 together with pKH3-wtβ-Cat orpKH3-β-Cat1-519 in a ratio of 1:20. Twenty-four hours after transfection, myoblasts were switched to the DM for 3 days and examined for myotube formation. GFP-expressing cells were counted as in Fig. 1A and B.