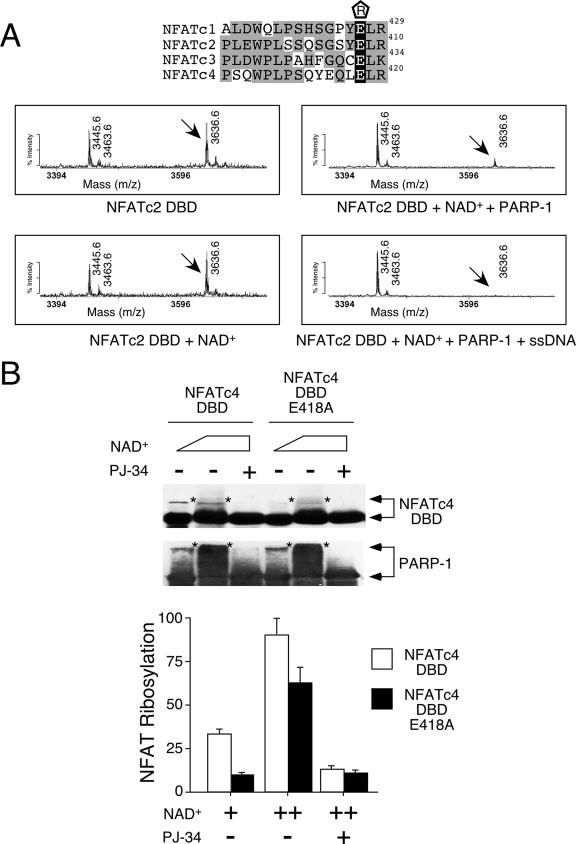
FIG. 4.
Conserved Glu residue on NFAT DBD is ADP-ribosylated by PARP-1. (A) Recombinant NFATc2 DBD was incubated with NAD+ in the presence and absence of purified PARP-1 and subjected to tryptic digestion and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry analysis. The effect of PARP-1 activator single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) was also determined. Target peptide 3636.6 was sequenced by tandem mass spectrometry to confirm its identity. The conserved Glu residues of NFAT members are highlighted in black in the sequence alignment above, with their positions given at the right. “R” enclosed in a pentagon above the sequences indicates ADP-ribosylation. Gray highlighting indicates similar amino acid sequences on the DBDs of different NFAT members. (B) Wild-type or Ala418 NFATc4 DBD expressed in COS cells was immunoprecipitated and incubated with increasing amounts of NAD+ in the presence of purified PARP-1. After incubation, NFAT DBD and PARP-1 were analyzed by immunoblotting analysis. The extent of ADP-ribosylation was revealed by the reduction in electrophoretic mobility of NFAT DBD and PARP-1 (top panel, indicated by asterisks). PARP-1 inhibitor PJ-34 was used to demonstrate specificity. The extent of [32P]ADP-ribose incorporation in NFATc4 DBD and PARP-1 was determined by using a PhosphorImager, and the results are presented in the bottom panel. +, present; ++, higher concentration present; −, absent.