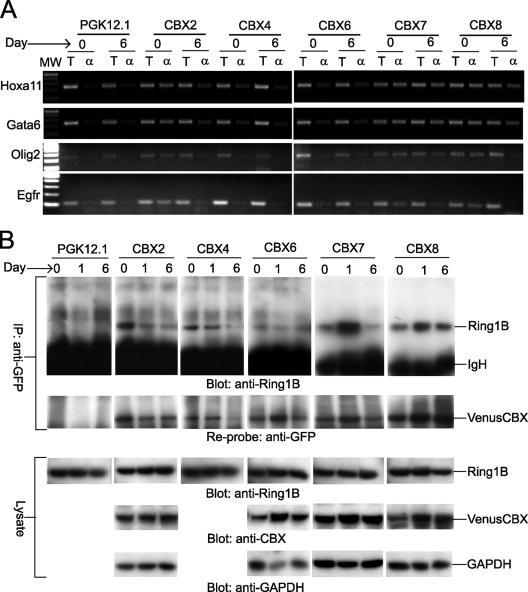
FIG. 1.
Analysis of CBX fusion protein binding to PcG target genes and interactions with endogenous Ring1B during ES cell differentiation. (A) Changes in CBX fusion binding to PcG target genes during ES cell differentiation. CBX fusion binding to Hoxa11, Gata6, Olig2, and Egfr promoters was evaluated before (day 0) and 6 days after inducing differentiation (day 6) of the CBX2#16, CBX4#11, CBX6#7, CBX7#9, and CBX8#1 ES cell lines using chromatin immunoprecipitation. The total chromatin (T) and chromatin precipitated by using anti-GFP antibody (α) were analyzed by using primers specific for each of the promoters. MW, molecular weight. The parental PGK12.1 ES cell line was used as a control. All reactions for each promoter were performed in parallel. (B) Interactions between CBX fusions and endogenous Ring1B during ES cell differentiation. Lysates prepared before (day 0) or 6 days after inducing differentiation (day 6) of the CBX2#16, CBX4#11, CBX6#7, CBX7#9, and CBX8#1 ES cell lines were precipitated by using anti-GFP antibody. The precipitates were analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Ring1B antibody (top panel). After detection, the blot was stripped and analyzed by using anti-GFP antibody (second panel) to determine the amounts of CBX fusions precipitated from the extracts. The cell lysates were also analyzed by Western blotting using anti-Ring1B antibody (third panel), antibodies against CBX2, CBX6, CBX7, or CBX 8 (fourth panel), and anti-GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) antibody (fifth panel). All precipitations and blots were performed in parallel. A shorter exposure of the anti-Ring1B blot of precipitates from the CBX7#9 and CBX8#1 lines is shown. The CBX4 fusion was not consistently detected by using available anti-CBX4 antibodies. IgH, immunoglobulin H; IP, immunoprecipitate.