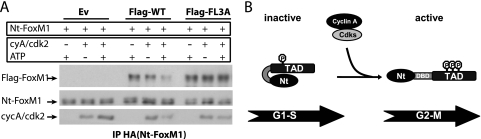
FIG. 8.
Autoinhibition of the FoxM1 transcriptional activity is released upon phosphorylation by active cyclin A/cdk2 complexes during G2. (A) The immunoprecipitates containing HA-Nt-FoxM1 and wild-type Flag-FoxM1 (Flag-WT) or HA-Nt-FoxM1 and Flag-FoxM13A mutant (Flag-FL3A) were incubated with commercial active cyclin A/cdk2 in the presence or absence of ATP. FoxM1 and cdk2 protein levels were viewed by Western blotting. (B) Model illustrating the cell cycle-dependent regulation of FoxM1 transcriptional activity. During G1/S, FoxM1 activity is repressed by its own N-terminal domain, most likely via direct interaction with the C-terminal TAD. As cells progress to the G2 phase, phosphorylation by cyclin A/cdk complexes promotes the inactivation of the N-terminal autorepressor domain by disrupting the interaction between the N terminus and the C-terminal TAD, allowing activation of the FoxM1 protein.