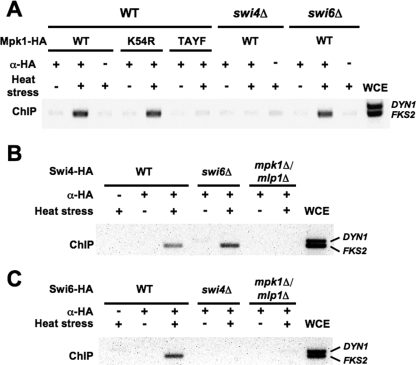
FIG. 4.
Interdependent recruitment of Mpk1 and Swi4 to the FKS2 promoter. (A) Genomic ChIP demonstrates that association of Mpk1-HA with the FKS2 promoter is dependent on Swi4 but not Swi6. Yeast strains (wild-type, DL3187; swi4Δ, DL3405; or swi6Δ, DL3233) were transformed with a multicopy plasmid bearing the indicated MPK1-HA allele and subjected to thermal stress prior to ChIP analysis as described in the legend of Fig. 3, except that strains were cultivated in the presence of 10% sorbitol. An additional primer pair for PCR amplification DYN1 sequence was included as a negative control. (B) Association of Swi4-HA with the FKS2 promoter is dependent on Mpk1/Mlp1 but not Swi6. Yeast strains (wild-type, DL3187; swi6Δ, DL3233; or mpk1Δ mlp1Δ, DL3183) were transformed with a multicopy plasmid bearing SWI4-HA (p2339) and treated as above. (C) Association of Swi6 with the FKS2 promoter is dependent on both Swi4 and Mpk1/Mlp1. Yeast strains (wild-type, DL3187; swi4Δ, DL3405; or mpk1Δ mlp1Δ, DL3183) were transformed with a multicopy plasmid bearing SWI6-HA (p2341) and treated as above. WCE, whole-cell extract; WT, wild type; α, anti; TAYF, mpk1-T190A Y192F.