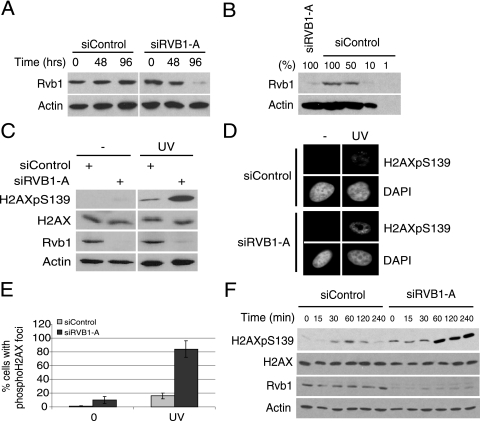
FIG. 1.
The depletion of Rvb1 increases phospho-H2AX after DNA damage. (A) Depletion of Rvb1 protein using siRNA against RVB1. Lysates prepared from HeLa cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs at the indicated times were immunoblotted for Rvb1 protein and β-actin. (B) Semiquantitative Western blot analysis of Rvb1. The indicated amounts of HeLa cell lysates were loaded and blotted with anti-Rvb1 and anti-β-actin antibodies. One hundred percent equals 20 μg of protein loaded. (C) Increase in total phospho-H2AX after DNA damage. Lysates from HeLa cells were prepared after the cells were transfected with siRNA with or without UV. UV irradiation was carried out 72 h after the transfection of cells with siRNA, and cells were harvested 60 min post-UV irradiation. Results from immunoblotting with anti-phospho-H2AX, anti-H2AX, anti-Rvb1, and anti-β-actin antibodies are shown. +, present; −, absent; H2AXpS139, H2AX phosphorylated on S139. (D) Immunofluorescence analysis with anti-phospho-H2AX antibody. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs and processed for immunofluorescence by using anti-phospho-H2AX antibody. DNA damage was induced as mentioned in the legend to panel C. (E) Quantitation of phospho-H2AX foci. The percentages of cells positive for phospho-H2AX foci among cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and those with (UV) and without (0) DNA damage in the analysis presented in panel D are shown. The experiment was repeated three times, and the means ± standard deviations (SD) are plotted. (F) The loss of Rvb1 results in the persistence of phospho-H2AX. HeLa cells were transfected with the indicated siRNAs. Cells were harvested at the indicated time points after UV irradiation, and lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.