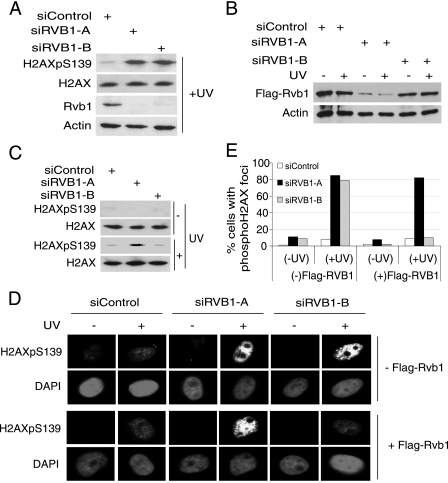
FIG. 2.
The Rvb1 knockdown phenotype can be reversed by the expression of exogenous Rvb1 protein. (A) The depletion of endogenous Rvb1 by siRVB1-A and siRVB1-B increases phospho-H2AX. HeLa cell lysates were prepared 72 h after the transfection of cells with the indicated siRNAs. The decrease in total Rvb1 protein was detected using anti-Rvb1 antibody, and anti-β-actin was used as a loading control. +, present; H2AXpS139, H2AX phosphorylated on S139. (B) Exogenous Flag-Rvb1 was knocked down by siRVB1-A but not siRVB1-B. HeLa cells stably expressing Flag-Rvb1 were lysed after transfection with the indicated siRNAs with (+) or without (−) UV irradiation. The experiment was carried out as described for panel A. (C) Phospho-H2AX levels after Rvb1 are restored by expressing Flag-Rvb1 resistant to siRVB1-B. HeLa cells stably expressing Flag-Rvb1 were transfected for 72 h with the indicated siRNAs before UV irradiation and immunoblotting of lysates with the indicated antibodies. (D) Phospho-H2AX foci detected by immunofluorescence. HeLa cells with or without Flag-Rvb1 were transfected with the indicated siRNAs for 72 h and either left untreated or irradiated with UV. +, present; −, absent. (E) Quantitation of phospho-H2AX foci. The percentages of cells positive for phospho-H2AX foci among cells transfected with the indicated siRNAs and those with (+UV) and without (−UV) DNA damage in the analysis presented in panel D are shown.