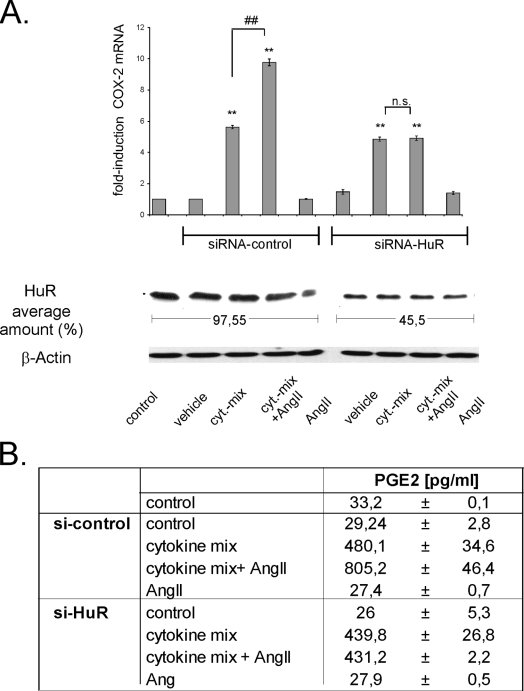
FIG. 6.
Silencing of HuR inhibits AngII-induced amplification of cytokine-stimulated COX-2 levels and PGE2 synthesis. (A) MC were left untransfected (control) or were transfected with either duplex siRNA of human HuR (siRNA-HuR) or, alternatively, with control duplex siRNA (siRNA-control) as described in Materials and Methods. After transfection, cells were serum starved for 16 h before being treated for a further 24 h with vehicle or with a cytokine mixture (cyt-mix) containing IL-1β and TNF-α (both at 2 nM) in the presence (+ AngII; 100 nM) or absence of AngII or with AngII alone, as indicated. The efficiency of silencing of HuR protein levels was monitored by assessment of the total HuR level by Western blot analysis using an anti-HuR-specific antibody and is depicted as the average amount of remaining HuR contents. To correct for variations in protein loading, the blot was stripped and probed with an anti-β-actin antibody Changes in the COX-2 mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR by normalizing COX-2 mRNA to GAPDH mRNA. The results are means ± SD (n = 3) and are presented as induction versus nonstimulated controls (**, P ≤ 0.01) or versus cytokine-stimulated values (##, P ≤ 0.01). n.s., not significant. (B) PGE2 levels in cell supernatants derived from hMC treated as indicated in panel A and described in detail in the legend to panel A. Data represent means ± SD (n = 3).