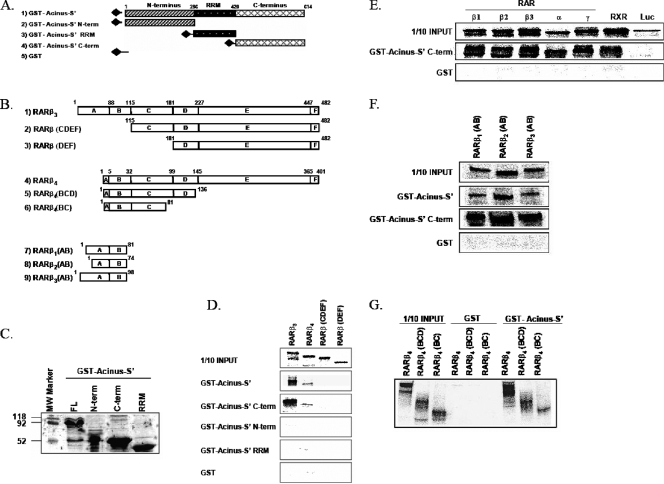
FIG. 5.
(A and B) Schematic representation of Acinus-S′ (A) and RARβ (B) deletion mutants used in GST pull-down assays to map the interaction domains. (C) Purification of GST-Acinus-S′ deletion mutants. GST fusion Acinus-S′ plasmid DNAs representing the full-length GST-Acinus-S′, GST-Acinus-S′ N terminus, GST-Acinus-S′ C terminus, and GST-Acinus-S′ RRM were expressed in E. coli BL21, purified using a glutathione-agarose affinity purification protocol, resolved by 12.5% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and visualized using Coomassie blue staining. Equal amounts of purified proteins were used for GST-pull down assays. (D) The C terminus of Acinus-S′ binds to the N terminus of RARβ. GST-Acinus-S′, GST-Acinus-S′ N terminus, GST-Acinus-S′ RRM, and GST-Acinus-S′ C terminus were incubated with in vitro-transcribed and -translated full-length [35S]methionine-labeled RARβ3, RARβ4, RARβ(CDEF), and RARβ(DEF). (E) Interaction of the C-terminal region of Acinus-S′ with RARs and RXRα. GST pull-down assays were performed using GST-Acinus-S′ C terminus and in vitro-transcribed and -translated [35S]methionine-labeled RARs (RARα1, RARβ1, RARβ2, RARβ3, RARγ2), RXRα, and luciferase. (F) The C terminus of Acinus-S′ binds to the A/B domain of RARβ. Full-length GST-Acinus-S′ and GST-Acinus S′ C terminus were incubated with in vitro-transcribed and -translated [35S]methionine-labeled A/B domains of RARβ isoforms [(RARβ1(AB), RARβ2(AB), and RARβ3(AB)]. (G) The C terminus of Acinus-S′ interacts with the B domain of RARβ. Interaction assays were performed with full-length GST-Acinus-S′ and in vitro-transcribed and -translated [35S]methionine-labeled RARβ4 and RARβ4 deletion mutants lacking the EF domain [RARβ4(BCD)] or lacking the DEF and partial C domains [RARβ4(BC)].