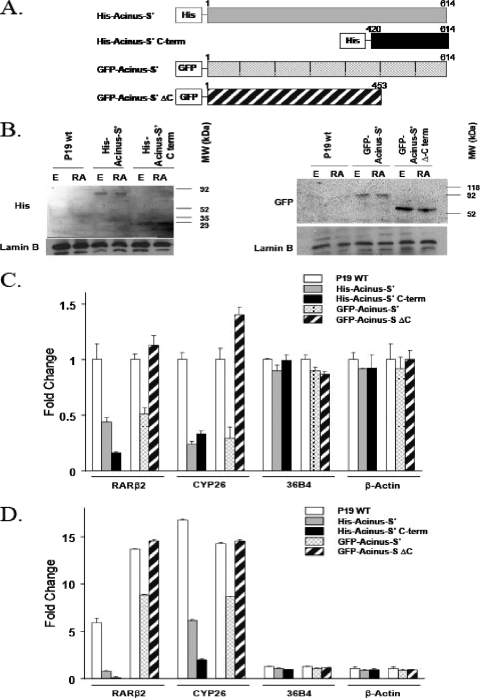
FIG. 6.
(A) Schematic representation of Acinus-S′ constructs used to determine the functional importance of the Acinus-S′ C-terminal domain. (B) Expression of Acinus-S′ C-terminal deletion mutants in P19 cells. P19 cells were plated on 100-mm tissue culture dishes and transfected with 10 μg of one of the following DNAs: His-Acinus-S′, His-Acinus-S′ C terminus, GFP-Acinus-S′, or GFP-Acinus-S′ ΔC. At 24 h after transfection, the cells were treated with ethanol (E) or 1 μM RA for 4 h and nuclear extracts were prepared. Western blot analysis was performed using primary anti-His or anti-GFP antibody followed by a secondary horseradish peroxidase-anti-rabbit antibody. Anti-lamin B primary antibody was used as a loading control. (C and D) Effect of the C-terminal end of Acinus-S′ on the expression of RAR-regulated genes in the absence (C) and presence (D) of RA. P19 cells were transfected and treated as described above. The expression levels of RAR-dependent genes (RARβ2 and CYP26A1) and control genes (36B4 and β-actin) were measured by real-time RT-PCR. The expression level of each gene examined was normalized to the endogenous GAPDH levels and expressed relative to the ethanol-treated P19 cells. Error bars indicate standard deviations.