FIG. 2.
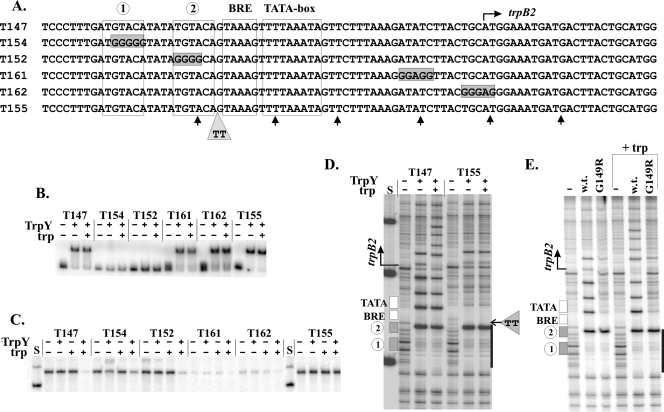
EMSA of TrpY binding, trpB2 transcription and DNase I footprint analysis of mutated DNA templates. (A) Sequences of the trpB2 regulatory region of the templates used, with the differences from the wild-type sequence (T147) identified. The locations of the DNase I-hypersensitive sites introduced into T147 by TrpY binding are indicated (↑). (B) EMSA of the complexes formed in reaction mixtures that contained 100 pM TrpY (+) and 1 fmol of 32P-labeled template DNA in the presence (+) or absence (−) of 24 μM tryptophan (trp). (C) trpB2 transcripts synthesized in single-round reaction mixtures, incubated for 5 min at 60°C, and assembled as previously described (21), in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 100 nM TrpY and the absence (−) or presence (+) of 24 μM tryptophan. Control lanes (S) contained size standards. (D) Electrophoretic separation of the DNase I digestion products of T147 and T155 generated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of TrpY at a 20:1 molar ratio of TrpY to DNA, with (+) or without (−) tryptophan (trp) present. The locations of the trpB2 regulatory elements and the 2-bp insertion in T155 are indicated. The heavy line identifies the TRP box region protected by TrpY binding, as shown in Fig. 1A. The control lane (S) contained size standards. (E) Electrophoretic separation of the DNase I digestion products of T147 generated in reaction mixtures lacking (−) or containing wild-type (w.t.) TrpY or TrpYG149R, at 20-to-1 molar ratios with the DNA, with (+trp) or without tryptophan present.