FIG. 1.
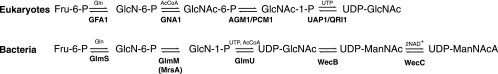
Eukaryotes use the Leloir pathway to produce UDP-GlcNAc (22). The yeast Gfa1p protein is a d-Fru-6-P amidotransferase that produces GlcN-6-P. The Gna1p acetyltransferase produces N-acetylglucosamine 6-phosphate (GlcNAc-6-P), which can be converted to GlcNAc-1-P by the Agm1p (Pcm1p) phosphomutase. Finally, the Uap1p (Qri1p) uridylyltransferase produces UDP-GlcNAc. Yeast cells can also incorporate exogenous glucosamine, using separate acetyltransferase and kinase enzymes. Bacteria use the GlmS amidotransferase, the GlmM phosphomutase, and the bifunctional GlmU acetyltransferase/uridylyltransferase enzymes to produce UDP-GlcNAc (21). The WecB epimerase and the WecC dehydrogenase make UDP-ManNAcA for enterobacterial common-antigen biosynthesis (in some gram-negative proteobacteria) and capsule formation (in some gram-positive bacteria).