Figure 8. Effect of aT57S and S52A amino acid substitutions on ability of alcohol to compete for ANS binding.
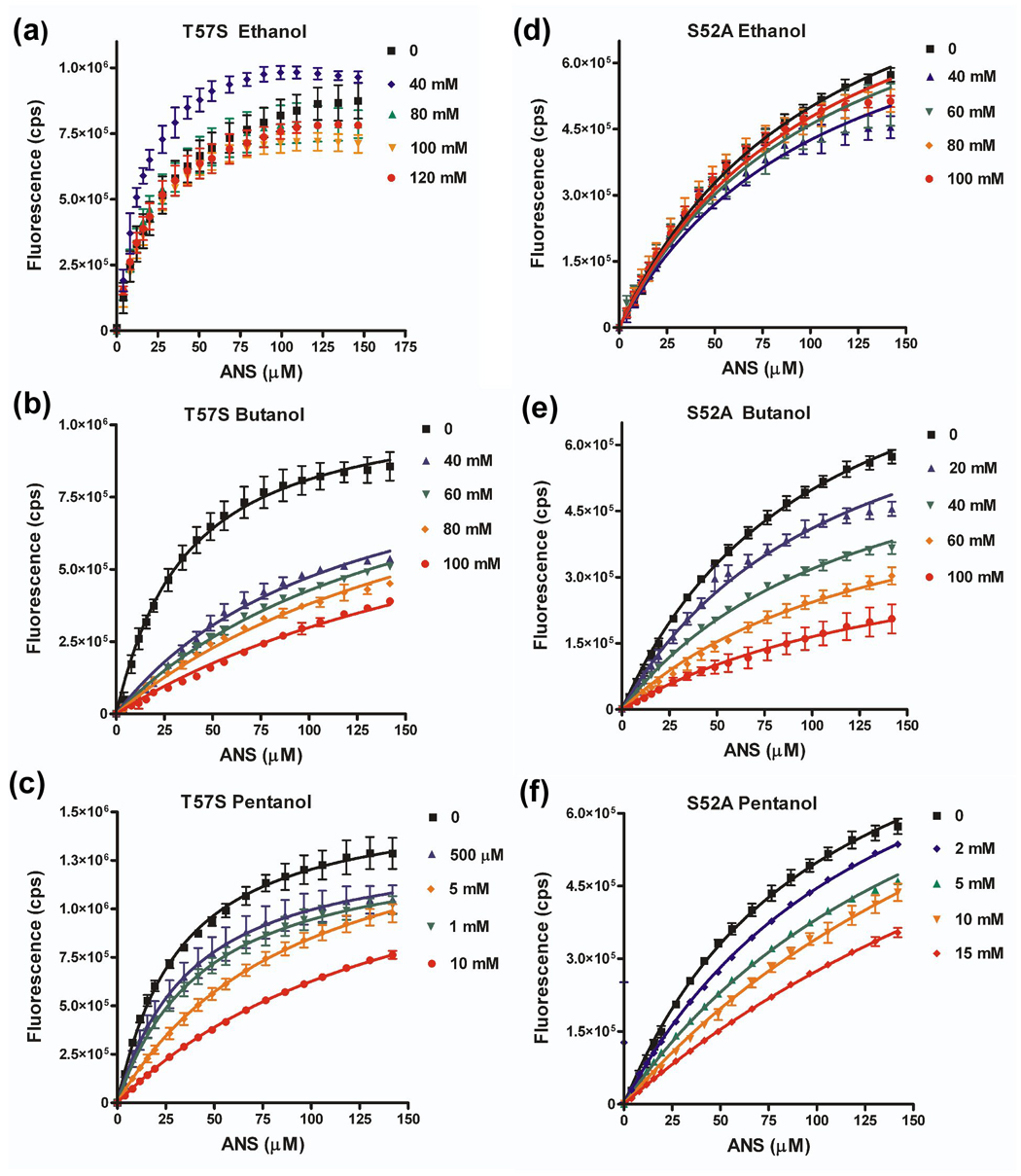
Binding isotherms for LUSH-alcohol complexes with ANS as a function of increasing alcohol concentrations for (a) T57S-ethanol, (b) T57S-butanol, (c) T57S-pentanol, (d) S52A-ethanol, (e) S52A-butanol, and (f) S52A-pentanol. Curves were fit in Graphpad Prism to a competitive binding isotherm as described in materials and methods. Ethanol could not compete for binding of ANS with either the T57S or S52A proteins. The concentration of alcohol is indicated
