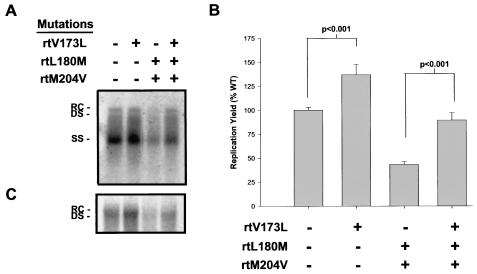
FIG. 3.
Replication yields of wild-type HBV and lamivudine-resistant HBV after transient transfection into HepG2 cells. (A) HepG2 cells were transfected with plasmids encoding wild-type, rtV173L, rtL180M and rtM204V, or rtV173L, rtL180M, and rtM204V HBV DNAs. HBV was allowed to replicate in the absence of drug for 1 week, after which replicative intermediates were isolated and analyzed by Southern blotting. Relaxed circular (RC), double-stranded (DS), and single-stranded (SS) forms of HBV DNA are indicated. (B) Three experiments were performed in triplicate, and the mean levels of viral replication relative to those of the wild type (WT) are plotted (error bars indicate standard errors). HBeAg, which is secreted from the input plasmid DNA, was used to normalize transfection efficiency. Paired t tests were used to compare replication levels between wild-type and rtV173L HBVs and between rtL180M-rtM204V and rtV173L-rtL180M-rtM204V HBVs; P values are indicated. (C) In a subsequent experiment, the secretion of mature HBV virions was measured by extraction of extracellular HBV DNA from media conditioned with transfected cells and Southern blot analysis.