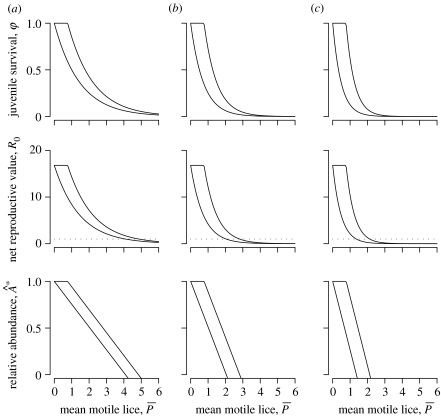
Figure 3.
Effects of increasing motile sea lice infection, , of juvenile pink salmon on juvenile salmon survival from parasites (φ), salmon net reproductive value (R0) and equilibrium abundance relative to abundance at natural sea lice levels for (a) one-month exposure, (b) two-month exposure and (c) three-month exposure to the parasites. Model predictions are bounded by compensatory (right boundary, equation (5.3)) and non-compensatory (left boundary, equation (5.2)) parasite-induced host mortality. The horizontal dotted line shows R0=1, above which salmon populations persist and below which salmon populations collapse.