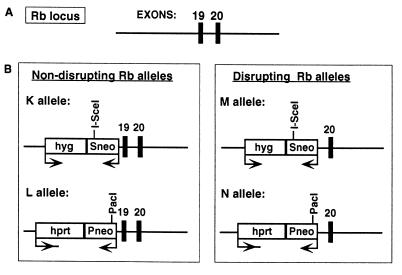
Figure 1.
Gene-targeted region of the Rb locus in ES cells containing recombination substrates. (A) The Rb locus at exons 19 and 20. (B) Gene-targeted Rb alleles containing substrates to detect DSB-induced allelic recombination. Alleles K and L are nondisrupting Rb alleles that have the recombination substrates gene targeted to intron 18. Alleles M and N are disrupting Rb alleles that have the recombination substrates targeted to exon 19. Each Rb allele contains a defective neo gene. The K and M alleles contain the Sneo gene that is mutated by the presence of an I-SceI site at the 3′ end of the neo gene. The 18-bp I-SceI site can be cleaved in vivo by expression of I-SceI. The L and N alleles contain the Pneo gene that is mutated at its 5′ end by the insertion of a PacI linker. Transcription of the neo genes is opposite to that of the Rb gene. Drug selection markers hyg+ and hprt+ are transcribed in the same orientation as the Rb gene and were used to select for gene targeting in the hprt− ES cell line. Single rounds of gene targeting were used to construct cell lines with each of the K, L, M, and N alleles. Consecutive rounds of gene targeting were used to construct cell lines with KL and MN alleles. The KL cell line is effectively Rb+/+, whereas the MN cell line is Rb−/−.