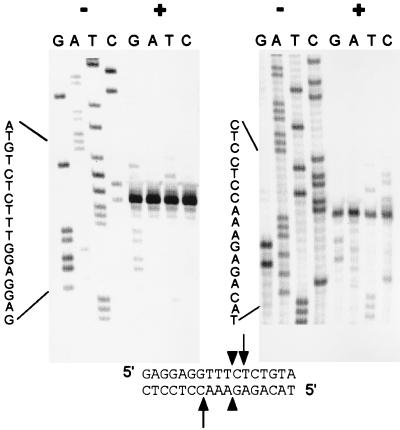
Figure 6.
The AnCOB intron-encoded protein is also a DNA endonuclease. Two DNA chain termination sequencing reactions were performed, one on either strand of a cDNA clone that spans the intron insertion site (Materials and Methods). Half of each reaction remained uncut (−) and the other half was digested (+) with the AnCOB protein preparation. Newly synthesized DNA molecules that terminate before reaching or completing the recognition site will remain uncut (including those that extend beyond the cleavage site but fail to complete the entire recognition site; see ref. 30). Strands that extend beyond the recognition site will all be cleaved and give the same-sized, primer-proximal, labeled fragment and a distal unlabeled fragment that will vary in size (the radioactive label is primarily incorporated very close to the primer; see Materials and Methods). Arrows indicate the cleavage sites and the arrowheads the site at which the intron would be inserted.