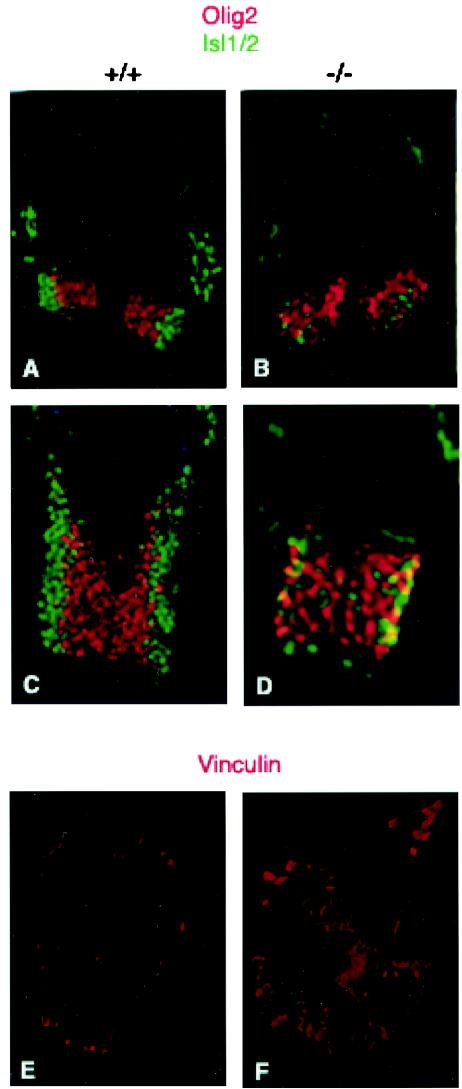
FIG. 4.
Defects in motor neuron and interneuron development in PAK4 knockout embryos. (A to D) Cross sections of different parts of the neural tubes from E9.5 embryos were stained with anti-olig2 (red) and anti-Isl1/2 (green) antibodies. Neural tubes from PAK4 wild-type (+/+) (A and C) and PAK4-null (−/−) (B and D) embryos were analyzed. There were fewer Is1/2-positive cells in the knockouts. Isl1/2-positive cells that were present in the knockouts were not in the correct lateral positions. (E and F) PAK4-deficient cells had increased levels of focal adhesions. Cells isolated from E9.5 PAK4+/+ (E) and PAK4−/− (F) embryos grown on glass coverslips were starved in serum-free medium for 24 h and then subjected to indirect immunofluorescence microscopy using antivinculin antibody. Whereas PAK4+/+ cells only contained low levels of vinculin when grown in serum-free medium, PAK4-null cells had large clusters of vinculin.