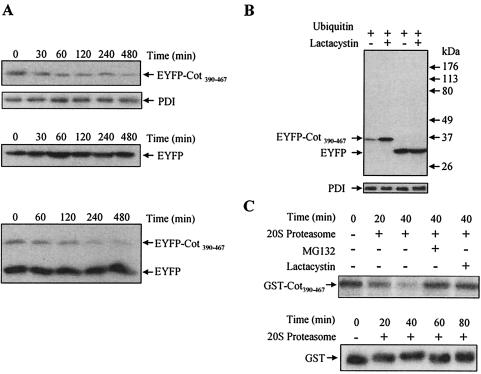
FIG. 5.
The C terminal of wt Cot triggers its degradation by the proteasome. (A) HEK293 cells 14.5 h after transfection with 10 μg of pEYFP-Cot390-467 or 10 μg of pEYFP or cotransfected with 5 μg of pEYFP-Cot390-467 together with 5 μg of pEYFP were further incubated with 100 μg of cycloheximide/ml for different times (0, 30, 60, 120, 240, and 480 min). The total extracts were Western blotted and probed with the anti-EYFP antibody. The figure shows one of two experiments performed in duplicate. (B) Total extracts of cells 14.5 h after transfection with 5 μg of pEYFP or 5 μg of pEYFP-Cot390-467 together with 5 μg of pCMV-His-ubiquitin and further incubated for 7.5 h in the presence or absence of 10 μM lactacystin. The extracts were Western blotted and probed with anti-EYFP. Similar results were obtained in two different experiments performed in duplicate. (C) Recombinant GST-Cot390-467 was subjected to in vitro degradation by the 20S proteasome for 20 and 40 min. GST-Cot390-467 was also incubated with 20S proteasome in the presence of 20 μM MG132 or 10 μM lactacystin. The different samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Western blotted to be probed with an anti-C-terminal Cot antibody. Similar results were obtained in three experiments performed in duplicate. Recombinant GST was subjected to in vitro degradation for 20, 40, 60, and 80 min by the 20S proteasome. The different samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting, which was probed with anti-GST antibody. Similar results were obtained in two experiments performed in duplicate.