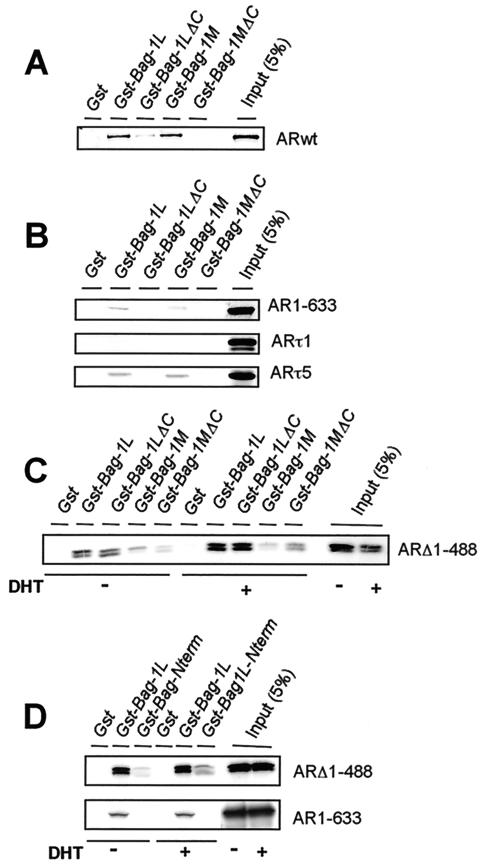
FIG. 3.
Bag-1L binds to the C- and N-terminal regions of the AR. Distinct domains of the AR interact with Bag-1L and Bag-1M. The human AR and various fragments of the receptor were translated in vitro, and the [32S]methionine-labeled translation products were incubated with glutathione-agarose beads to which GST, GST-Bag-1L, GST-Bag-1LΔC, GST-Bag-1M, or GST-Bag-1MΔC are bound. The beads were washed, and bound proteins were separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and detected by autoradiography. Portions of the 32S-labeled in vitro-translated proteins corresponding to 5% of the protein amounts used in the binding reactions were loaded onto the gel as input. (A to C) Interaction of Bag-1 proteins with the wild-type AR or NH2- or COOH-terminal fragments as well as the τ1 and τ5 fragments of the receptor; (D) binding of the Bag-1L N-terminal fragment to the COOH- but not the NH2-terminal sequence of the AR. In panels C and D, the in vitro-translated mutant AR ARΔ1-488 and AR1-633 were incubated with or without 10−7 M DHT before being used in the binding reaction.