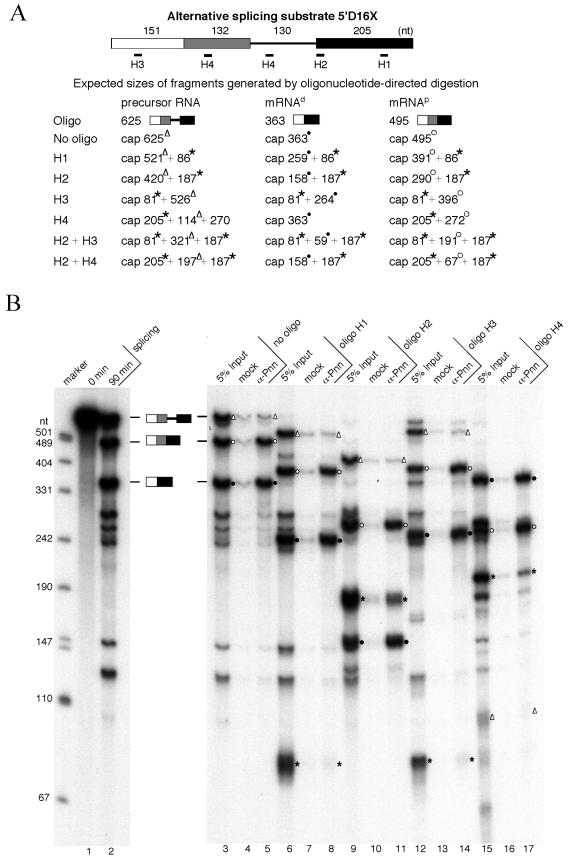
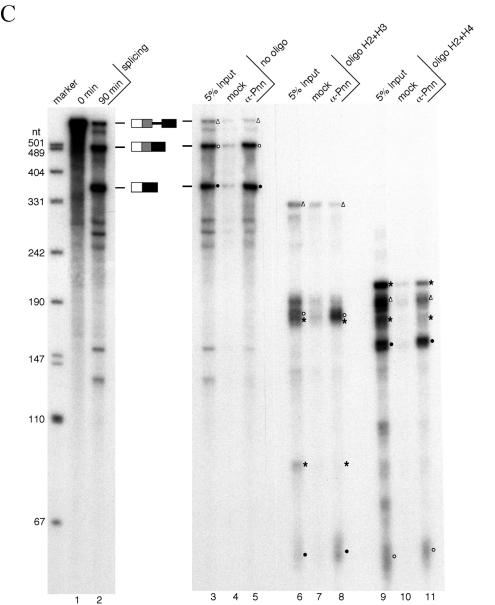
FIG. 2.
Pnn is associated with spliced mRNAs at the location immediately upstream of the exon-exon junction. (A) The 5′D16X pre-mRNA and the oligonucleotides used to direct RNase H cleavage are diagrammed. Note that oligonucleotide H4 anneals to a repeated sequence located in the intron and between the two 5′ splice sites (9). Expected sizes of the fragments generated by RNase H cleavage from the pre-mRNA and two alternatively spliced mRNAs (mRNAp and mRNAd) are listed. The mRNAp and mRNAd fragments carrying the region immediately upstream of the splice junction are labeled with open circles and solid circles, respectively. Open triangles indicate the fragments generated from the precursor RNA containing the site for EJC loading. Asterisks indicate the fragments that can be generated from both precursor and spliced mRNAs. (B) Single-oligonucleotide-directed RNase H digestion. The 5′D16X pre-mRNA was subjected to the splicing reaction at 30°C for 0 min (lane 1) or 90 min (lane 2). RNase H digestion was performed with 90-min splicing reactions in the absence of oligonucleotides (lanes 3 to 5) or in the presence of oligonucleotide H1 (lanes 6 to 8), H2 (lanes 9 to 11), H3 (lanes 12 to 14), or H4 (lanes 15 to 17). After digestion, immunoprecipitation was performed with mock (lanes 4, 7, 10, 13, and 16) or anti-Pnn (lanes 5, 8, 11, 14, and 17) antibodies. For comparison, 5% input of the reaction mixtures was loaded (lanes 3, 6, 9, 12, and 15). Size markers are as described in the legend for Fig. 1B. (C) RNase digestion with two oligonucleotides. Similar experiments were carried out as described for panel B except that oligonucleotides H2 and H3 (lanes 6 to 8) or H2 and H4 (lanes 9 to 11) were added simultaneously.