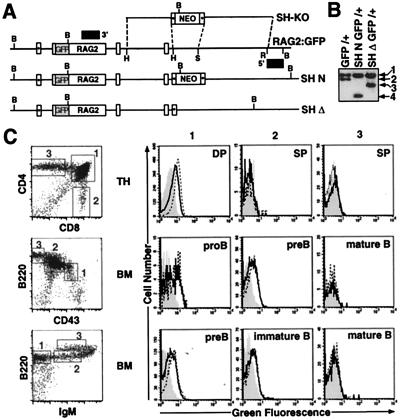
Figure 4.
RAG2:GFP expression in SHΔ-RAG2:GFP chimeric mice. (A) Targeting of the RAG2:GFP ES cell line with the SH-KO vector (as described in the legend of Fig. 3A). The RAG2:GFP knock-in allele (RAG2:GFP) is depicted with the SH-KO vector and alleles in which the SH region has been replaced with either the PGK-neor gene (SH N) or a single loxP site (SH Δ), following Cre-mediated deletion. (B) Southern blot analysis with the 3′ probe on BamHI-digested DNA isolated from (i) RAG2:GFP knock-in ES cells (GFP/+), (ii) GFP/+ ES cells in which the SH region was targeted and replaced on the GFP allele with the PGK-neor gene (SH N GFP/+), and (iii) SH N GFP/+ ES cells following Cre-mediated deletion of the PGK-neor gene (SH Δ GFP/+). 1, RAG2 wt allele (18 kb); 2, RAG2:GFP allele (15 kb); 3, SHΔ GFP allele (11 kb); 4, SH N GFP allele (7 kb). (C) Thymocytes (TH) and BM from wild-type mice and from RAG2:GFP and SHΔ-RAG2:GFP chimeric mice were stained with (i) PE-anti-CD4 and CyC-anti-CD8, (ii) PE-anti-CD43 and CyC-anti-B220, or (iii) PE-anti-IgM and CyC-anti-B220 and analyzed by FACS. Representative FACS plots are shown to illustrate gated populations, as there were no differences in development between wild-type and chimeric mice. For each of the gated TH and BM populations (as numbered), histograms for green fluorescence were generated. WT histograms (shaded) were overlayed with RAG2:GFP histograms (open dashed-line) and SHΔ-RAG2:GFP histograms (open solid line). Developmental T and B cell stages are indicated for each set of histograms.