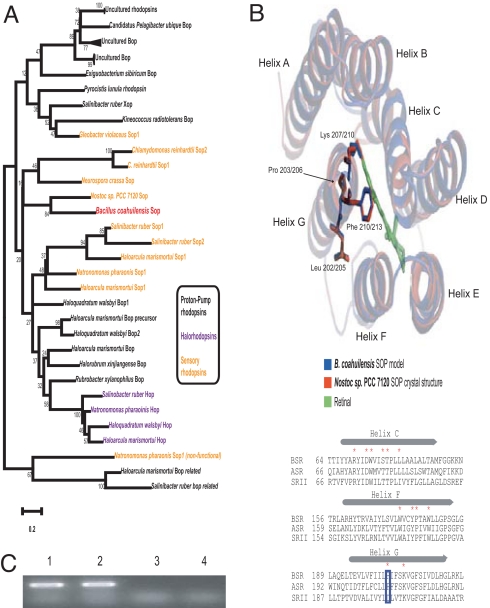
Fig. 3.
B. coahuilensis contains a sensory bacteriorhodopsin possibly acquired from cyanobacteria through an ancient HGT event. (A) Neighbor-joining tree showing the phylogenetic diversity of rhodopsins (31). (B) Bsr possesses all of the residues involved in retinal binding and was modeled (32) to the predicted structures of Anabaena and Natronomonas pharaonis. Alignment of segments of SR from B. coahuilensis (BSR, BM4401574), Anabaena sp. PCC7120 (ASR, PDB ID code 1XIO), and Natronomonas pharaonis DSM2160 (SRII, PDB ID code 1JGJ) show conservation of residues in the retinal-binding pocket (marked with asterisks) except for a Pro residue (positions BSR203 and ASR206), which is an Asp residue in all other microbial rhodopsins (blue rectangle; alignment adapted from ref. 10). Diagrammatic representation was done by using PyMol (http://www.pymol.org). (C) bsr is expressed in B. coahuilensis grown either under white light or in the dark. RT-PCR was carried out by using RNA obtained from bacteria grown under dark or white-light conditions (lanes 1 and 2, respectively). Lanes 3 and 4 are controls without reverse transcriptase.