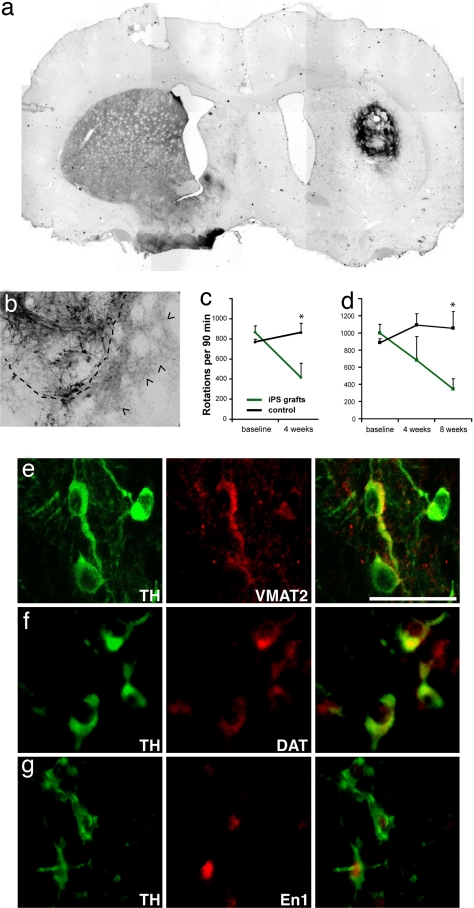
Fig. 5.
iPS cell-derived neurons integrate into the striatum of hemi-parkinsonian rats and improve behavioral deficits. (a) Overview of an iPS cell graft 4 weeks after transplantation stained with antibodies against TH (dark brown). (b) Higher magnification of another graft showing TH-positive soma and the dense innervation of the surrounding host striatum by donor-derived neurites (arrowheads). The dashed line indicates the edges of the graft. (c) Amphetamine-induced rotations are significantly reduced in animals grafted with unsorted iPS cell populations (green, n = 5) compared with the sham control animals (black, n = 10) (P = 0.0185, unpaired Student's t test). Shown are the number of rotations in 90 min after amphetamine injection as means and standard deviations. (d) Amphetamine-induced rotations in animals transplanted with iPS cell cultures after elimination of SSEA1-positive cells by FACS. Grafted animals (green, n = 4) show significant recovery compared with control animals (black, n = 10) (P = 0.006). (e–g) The grafted TH-positive cells (green) can be colabeled (red) with antibodies against VMAT2 (e), DAT (f), and En1 (g). (Scale bar: 50 μm.)