Fig. 1. Analysis of the xTsg2 cDNA and protein sequence.
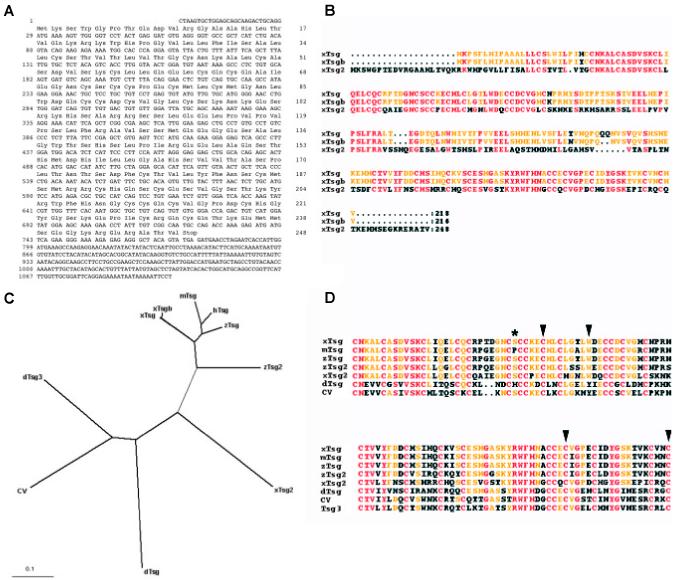
(A) Nucleotide and amino acid sequence of xTsg-2. (B) Alignment of the two pseudoalleles of xTsg with xTsg-2. (C) Dendrogram showing the phylogenic relations between the Xenopus (xTsg, xTsgb, xTsg-2), mouse (mTsg), human (hTsg), zebrafish (zTsg, zTsg-2) and Drosophila Tsg proteins (dTsg, cv/dTsg2, dTsg3). (D) ClustalW alignment of the indicated protein sequences demonstrating the conservation of amino acids required for ventralizing activity or chordin binding (arrowheads) and the position of an in vivo glycosylation site (asterisk). The accession numbers of the sequences used for the alignments were for xTsg, AF245221; xTsgb, AF279246; xTsg-2, BJ075535; mTsg, AAG00605; hTsg, NP_065699; zTsg, AAK27324; zTsg-2, AAK13255; dTsg, A53836; cv, CG12410; dTsg3, CG11582.
