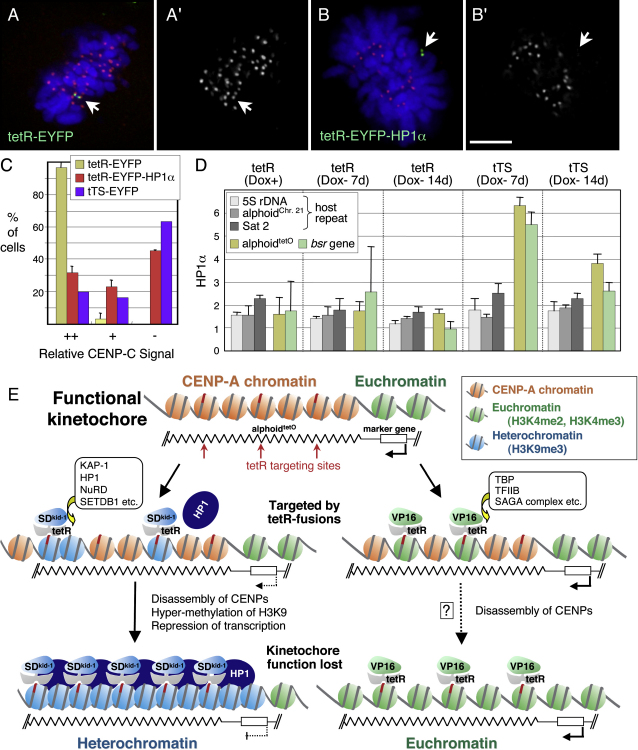
Figure 8.
HP1α Recruitment Inactivates the AlphoidtetO Kinetochore
(A) A duplicated HAC at metaphase has bound tetR-EYFP and CENP-C.
(B) A duplicated HAC at metaphase has bound tetR-EYFP-HP1α, but lacks CENP-C. Bar in (B′) = 5 μm for (A and B).
(C) Quantitation of the effects of expression of tetR-EYFP, tetR-EYFP-HP1α, and tTS-EYFP on the levels of CENP-C at kinetochores.
(D) AB2.2.18.21 cells expressing tetR or tTS were cultured in doxycycline-free medium for 7 or 14 d and analyzed by ChIP with anti-HP1α antibody. The tTS induces targeting of HP1α to both the alphoidtetO array and the adjacent marker gene. The decrease seen at 14 d likely reflects loss of the HAC. Error bars indicate SD (n = 2–3).
(E) Inactivation of the kinetochore by modulating the epigenetic status of the underlying chromatin. Centromere chromatin containing CENP-A (red) and H3K4me2 (not shown here) assembles on the alphoidtetO dimer array of the HAC, forming an active kinetochore structure. The chromatin of the marker gene contains H3K4me3 (green). Binding of the tTS (tetR-SDkid-1) induces H3K9 trimethylation (blue) at its target sites (red rectangle and arrow) on the alphoidtetO HAC. The resulting remodeling and compaction of the chromatin is incompatible with the structure of CENP-A chromatin and CENP-A quickly disappears from the heterochromatic alphoidtetO array. The centromere/kinetochore is inactivated. tTA (tetR-VP16) binding induces formation of open chromatin at the target site. In some cases, the open chromatin structure (euchromatin) somehow disrupts the CENP-A chromatin. However, in the case of tTA, the degree of HAC inactivation was less than that seen with the tTS. This suggests that the core of CENP-A chromatin is less sensitive to chromatin opening induced by VP16 and that in many cases HACs with open chromatin can still maintain a functional kinetochore. The data presented suggest an epigenetic mechanism to regulate the kinetochore activity based in part upon antagonism between centromere chromatin rich in CENP-A and H3K4me2 and heterochromatin rich in H3K9me3.