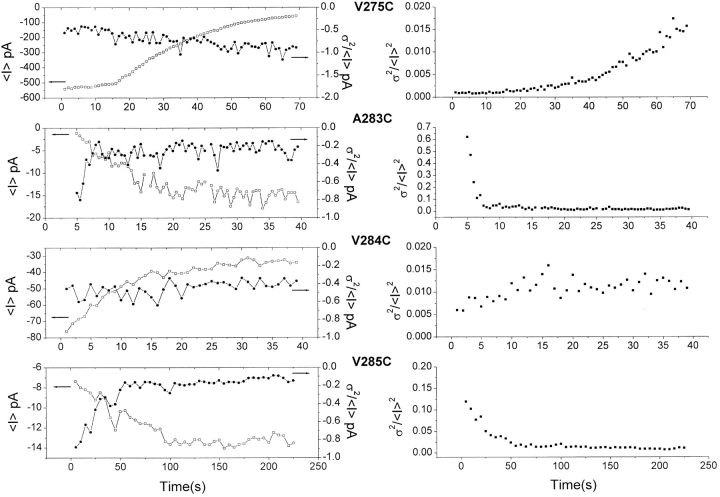
Figure 5.
Nonstationary noise analysis of the interacting MTSET-IKCa mutants. Relationship between the current variance σ2 and the mean current <I> during MTSET application illustrated for the V275C, A283C, V284C, and V285C mutants. <I> and σ2 were measured on successive time periods of 1 s for A283C, V284C, and V285C and 0.5 s for V275C. The V275C mutant displayed a constant σ2/<I> (left panel right scale) ratio despite an important decrease in <I> (left panel left scale), indicating an important inhibition of the channel unitary current. This proposal is also supported by the fact that the ratio σ2/<I>2 (right panel) increases in this case with a time constant equal to τi, the inhibition time constant measured for <I>. A similar noise pattern was also observed with the V284C mutant, although in this case the variations in σ2/<I> and σ2/<I>2 can be accounted for a partial inhibition of the channel unitary current plus a decrease in channel open probability. A different noise behavior is, however, observed with the A283C and V285C channels. The decrease in σ2/<I>2 observed with A283 correlates the increase in mean current with the σ2/<I> ratio remaining constant for time >7.5 s. This noise pattern would be compatible with a system where PB > PO with PO and PB << 1, thus supporting a model whereby the action of MTSET consists either to increase the channel open probability or recruit silent A283C mutants. The results obtained with V285C follow a similar pattern, although in this case the fact that the measured variation in σ2/<I>2 is more important than the mean current increase favors a system where PB > PO with PO << 1.