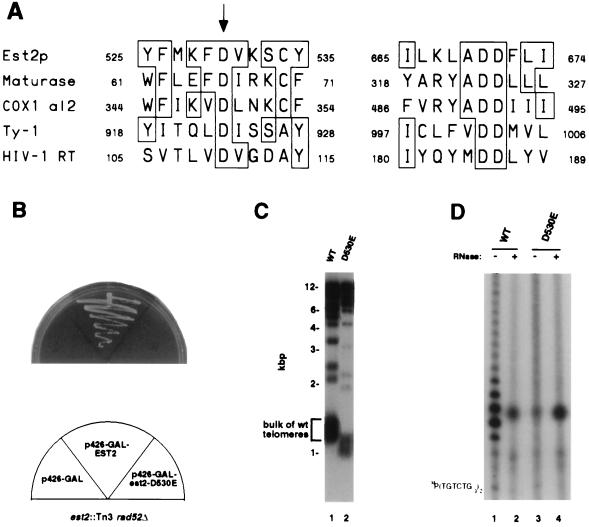
Figure 3.
Reverse transcriptase homology of Est2p is essential for telomerase function. (A) Homology between reverse transcriptase catalytic residues and Est2p. Alignment of regions of Est2p containing the conserved reverse transcriptase motifs A and C (36), or 3 and 5 (37) with the same regions of Arabidopsis maturase, S. cerevisiae COX1 group II intron 2 and retrotransposon Ty-1, and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (36, 37). Boxes denote residues conserved with Est2p. The three aspartic acid residues conserved among all the proteins shown are completely invariant among all RNA-dependent DNA polymerases (36, 37). The arrow denotes the Asp-530 residue that was mutagenized. (B) Failure of the D530E mutant to rescue inviability of est2 rad52 mutants. est2 rad52 mutant yeast were transformed with the negative control plasmid p426-GAL (left), with a positive control p426-GAL expressing wild-type EST2 (center), and with a p426-GAL plasmid expressing the D530E mutant (right). Loss of viability in the unrescued yeast is immediate, not delayed, because the est2 rad52 mutants have already been passaged ≈30 generations in culture. (C) Telomere shortening in est2 yeast expressing D530E mutant but not wild-type EST2. Telomere hybridization analysis of XhoI-digested genomic DNA isolated from an EST2 control (lane 1) or from est2 mutants expressing the D530E mutant (lane 2). (D) Lack of telomerase activity in yeast expressing the D530E mutant. Telomerase activity was assayed in extracts from an EST2 wild-type control (lanes 1 and 2) or from yeast expressing the D530E mutant (lanes 3 and 4). Extracts were pretreated with RNase (lanes 1 and 3) or left untreated (lanes 2 and 4). Position of the γ-32P-labeled primer is shown on the left.