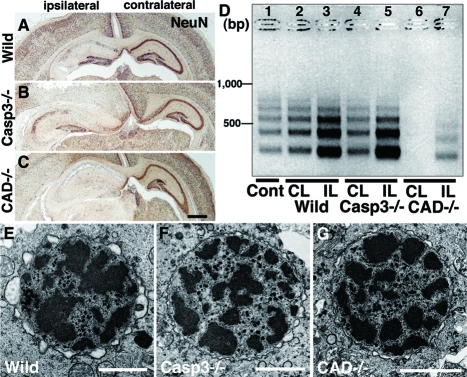
Figure 2.
Pyramidal neuron death in the hippocampus of neonatal mouse brains after H/I injury. A–C: Coronal histological sections of wild-type (Wild) (A), caspase-3-deficient (Casp3−/−) (B), and CAD-deficient (CAD−/−) (C) brains including ipsilateral and contralateral hippocampi 24 hours after H/I injury. Staining with NeuN. D: Genomic DNA fragmentation detected by LMPCR. Samples were obtained from the hippocampus of an untreated wild-type brain (Cont) (lane 1), and the contralateral (CL) and ipsilateral (IL) hippocampi of wild-type (lanes 2 and 3), caspase-3-deficient (lanes 4 and 5), and CAD-deficient (lanes 6 and 7) brains 24 hours after H/I injury. E–G: A nucleus with small patches of chromatin clumping was observed in the pyramidal neurons of not only wild-type (E) but also caspase-3-deficient (F) and CAD-deficient (G) mouse hippocampi 8 hours after H/I injury. Scale bars: 500 μm (C); 2 μm (E–G).