Figure 1.
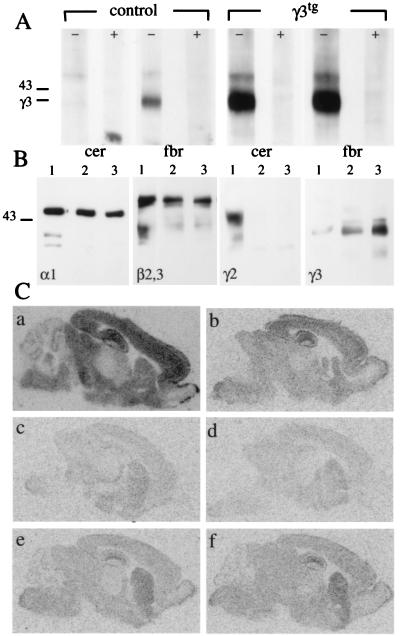
Expression of γ3 subunit and reconstitution of BZ binding sites in γ3tg/γ20/0 brain. (A) Western blot of γ3 subunit in membranes from cerebellum (cer) and forebrain (fbr) of adult γ2+/+ (control) and γ3tg/γ2+/+ (γ3tg) mice using a γ3 subunit-specific antiserum. Lanes marked with + indicate competition by antigenic peptide (10 μg/ml). Note the low level of γ3 subunit expression in forebrain and the lack of a signal in wt cerebellum. In contrast, the γ3 subunit is abundant in both parts of transgenic brain. The molecular mass (in kDa) of a standard and the position of the γ3 subunit are indicated. (B) Western blot of GABAA receptors immunoprecipitated from brain membranes with an α1 subunit antiserum. Lanes from γ2+/+ (1), γ20/0 (2), and γ3tg/γ20/0 (3) animals were labeled with the Abs indicated. Note the graded up-regulation of the γ3 subunit in γ20/0 and γ3tg/γ20/0 mice. (C) Distribution of total and zolpidem-insensitive BZ binding sites in γ2+/+ (a and b), γ20/0 (c and d), and γ3tg/γ20/0 brain (e and f) as seen by autoradiography with [3H]flumazenil (a, c, and e) or with [3H]flumazenil and 10 μM zolpidem (b, d, and f). Note that nearly all BZ binding sites remaining in γ20/0 mice are zolpidem-insensitive (d), suggesting that they represent GABAA receptors containing the γ3 subunit. In γ3tg/γ20/0 mice, there is a marked increase in BZ binding sites that are likewise zolpidem-insensitive (e and f).