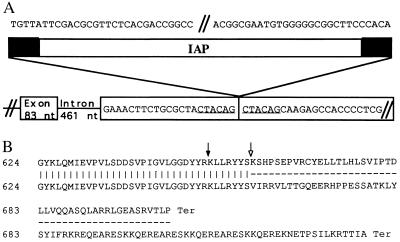
Figure 4.
Consequences of the ep IAP insertion. (A) DNA sequence of the IAP chromosomal insertion point. Six base pairs of mouse genomic target DNA (underlined) are duplicated at the site of the IAP element insertion within a 3′ exon. The IAP element depiction has black boxes representing long terminal repeat sequences, portions of which are shown above. Sequence of the larger genomic region (not shown; accession nos. AF003868 and AF004352) indicate that the ep gene and the IAP element are in opposite transcriptional orientations. (B) Predicted C-terminal amino acid sequences from ep and wild type. The sequence of the C terminal region of the wild-type ep protein is shown on the top line; the dark arrow marks the junction between the two adjacent exons shown above in A, and the open arrow indicates the beginning of the ORF predicted by IAP sequences. The sequence of the mutant ep protein is shown on the bottom lines. The amino acid sequences shown were deduced from the nucleotide sequences of the 3′ RACE products from wild type (accession no. AF003866) and ep (accession no. AF003867).