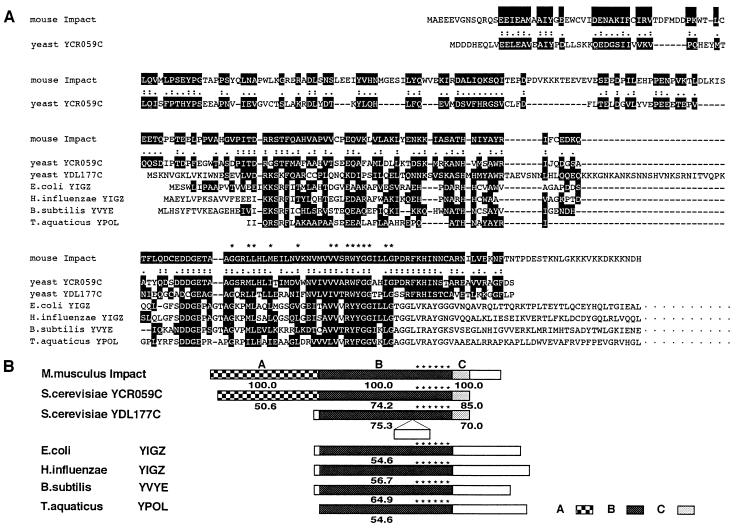
Figure 3.
Structure of predicted Impact gene product. (A) Amino acid homology between the predicted Impact gene product (GenBank no. D87973) and other hypothetical proteins, including Saccharomyces cerevisiae YCR059C (Swiss-Prot no. P25637), S. cerevisiae YDL177C (Protein Identification Resource no. S61035), E. coli YIGZ (Swiss-Prot no. P27862), H. influenzae YIGZ (Swiss-Prot no. P44842), B. subtilis YVYE (Swiss-Prot no. P32437), and T. aquaticus YPOL (Swiss-Prot no. P32438). Amino acid residues similarly conserved between putative Impact product and other hypothetical proteins are shaded. (B) Schematic presentation of members of the YCR59c/yigZ hypothetical protein family (PROSITE no. PS00910). The region B is the core region that is highly conserved among mouse, yeast, and various bacterial hypothetical proteins, and contains a characteristic signature G-x(2)-[LIMV](2)-x(2)-[LIMV]-x(4)-[LIMV]-x(5)-[LIMV](2)-x-R-[FYW(2)-G-G-x(2)-[LIMV]-G (PROSITE no. PDOC00707) shown by the asterisks. Regions A and C are common only between mouse and yeast hypothetical proteins. The number below each box is the similarity expressed in percentile to the corresponding region of putative Impact product.