Figure 1.
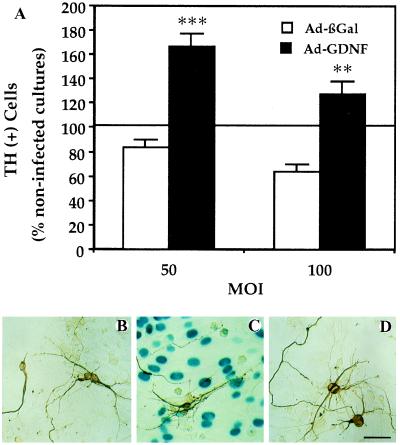
Increased survival of DA neurons in cultures infected with Ad-GDNF. (A) DA-cell counts by TH immunocytochemistry. Embryonic mesencephalic cells (100,000 cells per cm2) were plated on a layer of primary astroglial cells (100,000 cells per cm2) previously infected with Ad-GDNF or Ad-βGal. DA cells were identified with TH immunocytochemistry and counted. The values represent the percentages of total DA cells counted in noninfected cultures (means ± SEM of three determinations). In the control noninfected cultures, there were 982 ± 47 DA cells per well. ∗∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001 versus Ad-βGal. (B–D) Differentiation of DA neurons visualized by TH immunocytochemistry. Photomicrographs illustrating the morphology of DA cells plated on a layer of primary astroglial cells previously or not infected. (B) Noninfected astrocytes, (C) astrocytes infected with Ad-ßGal (50 pfu per cell), (D) with Ad-GDNF (50 pfu per cell). βGal expression is visualized enzymatically with 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl β-d-galactoside as a substrate giving rise to a blue color. Note that the differentiation of DA neurons is much more advanced in cultures producing the transgenic GDNF than in control or Ad-βGal-infected cultures. (Bar = 100 μm.)