Figure 7.
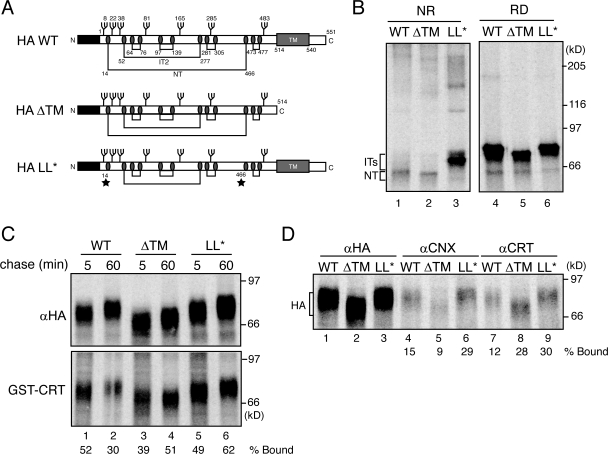
GT1 reglucosylates terminally nonnative HA. (A) Schematic of WT HA, HA with a premature stop codon at aa 514 (HA-ΔTM), and HA Cys14Ser/Cys466Ala (HA-LL*). All three constructs contain seven N-linked glycosylation sites. Both HA WT and HA-ΔTM have the capacity to form six disulfide bonds and the three oxidative forms of HA (IT1, IT2, and NT), whereas, HA-LL* is lacking the Cys (ovals) involved in the large loop disulfide (stars). (B) HA constructs were transiently overexpressed in wild-type CHO cells and radiolabeled for 10 min. HA was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates with HA antisera and analyzed via both nonreducing and reducing SDS-PAGE. (C) HA was expressed, as in B, in MI8-5 cells. Cells were radiolabeled for 10 min in the presence of 4 mM DTT and chased for the indicated time periods. HA was isolated by immunoprecipitation with HA antisera or by GST-calreticulin (GST-CRT) pulldown. Quantifications represent the percent bound to GST-calreticulin relative to the total immunoprecipitated HA. (D) HA was analyzed as in C. Cells were radiolabeled for 10 min in the presence of 4 mM DTT and chased for 60 min under nonreducing conditions. HA was isolated by immunoprecipitation with HA, calnexin (αCNX), or calreticulin (αCRT) antisera. Samples were resolved by 7.5% reducing SDS-PAGE and visualized by phosphorimaging. Quantifications represent the percent binding of the total immunoprecipitated HA to the lectin chaperones.