Table 2. CGGR variables, parameters and constants.
| Genetic Parameters | units | |
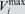
|
Maximum transcription initiation rate of the i-th gene class | 1/min |
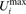
|
Maximum translation initiation rate of the i-th gene class mRNA | 1/min |
| Km,i | Binding affinity of RNAp holoenzyme to the i-th gene class promoter | 1/(µm)3 |
| Lm,i | Binding affinity of the 30S ribosome subunit to the i-th gene class mRNA RBS | 1/(µm)3 |
| tc,i | Average time to transcribe the i-th gene class ( = Li/ci) | min |
| tl,i | Average time to translate the mRNA of the i-th gene class ( = Li/3cp) | min |
| mi,j | Map location of the j-th gene in the i-th gene class | dimensionless |
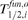
|
Functional half-life for the i-th gene class mRNA in the absence of ribosomes | min |
| Vini | Initiation volume | (µm)3 |
| Cell state variables | ||
| nRNAp | Concentration of total RNAp | 1/(µm)3 |
| nRNAp,free | Concentration of free functional RNAp | 1/(µm)3 |
| nribo | Concentration of total ribosomes | 1/(µm)3 |
| nribo,free | Concentration of free functional (30S) ribosomes | 1/(µm)3 |
| nbulk | Concentration of bulk protein | 1/(µm)3 |
| α | Specific growth rate (α = μ·ln(2), where μ is the doubling rate) | 1/min |
| Parameters and constants for the unconstrained CGGR | ||
| cribo/load | Production cost of one ribosome or load protein | dimensionless |
| n0 | Minimum cell density | 1/(µm)3 |
| Parameters and constants for the constrained CGGR | ||
| Mbulk | Bulk protein cutoff | 1/(µm)3 |
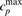
|
Maximal elongation rate | aa/min |
| h | Hill coefficient | dimensionless |
| Other parameters, variables and constants | ||
| cp | Peptide chain elongation rate | aa/min |
| ci | RNA chain elongation rate of the i-th gene class | bp/min |
| C | C period | min |
| di | Gene concentration of the i-th gene class | 1/(µm)3 |
| Li | Length of the i-th gene class | base pairs |
| vk | Volume of a macromolecule belonging to the k-th species | (µm)3 |
| Φ | Macromolecule volume fraction = Vmacro/Vcell | dimensionless |
Genetic parameters, cell state variables, and other variables and constants associated with the CGGR models. Gene classes labeled by index i include: rrn, r-protein, bulk protein and any load genes.
