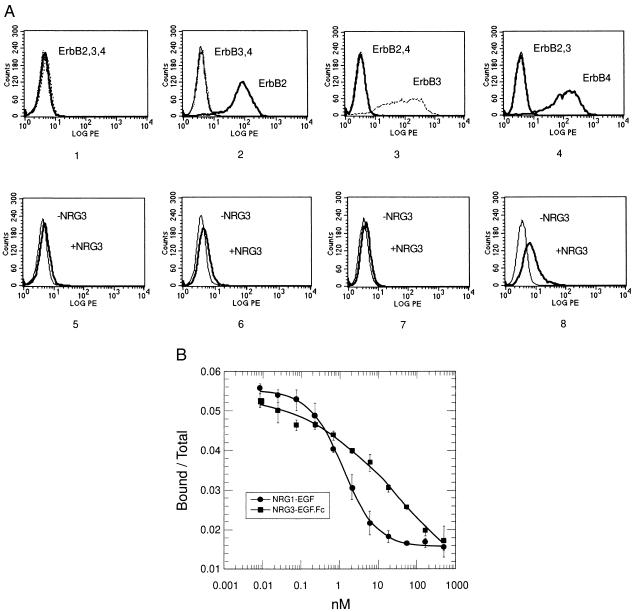
Figure 4.
Binding of NRG3EGF.Fc to ErbB4. (A) Binding of NRG3EGF.Fc to K562erbB cells as analyzed by FACS. (Panels 1-4) Parental K562 cells (1) or K562 cells expressing either ErbB2 (K562erbB2 cells, 2), ErbB3 (K562erbB3 cells, 3), or ErbB4 (K562erbB4 cells, 4) were examined for the expression of corresponding receptors. Cells were incubated with anti-ErbB2, anti-ErbB3, or anti-ErbB4 antibodies as indicated before the phycoerythrin-conjugated secondary antibody was added. The binding of antibodies was analyzed by FACS. LOG PE, relative fluorescent intensity; Counts, cell numbers. (Panels 5-8) NRG3EGF.Fc binds to ErbB4 expressing cells. Parental K562 cells (5), K562erbB2 cells (6), K562erbB3 cells (7), and K562erbB4 cells (8) were incubated with or without NRG3EGF.Fc (containing gD tag) for 1 hr, followed by anti-gD-tag primary antibody and phycoerythrin-conjugated secondary antibody. The binding of antibodies was evaluated by FACS analysis. (B) Competitive inhibition of 125I-NRG3EGF.Fc binding to immobilized ErbB4.Fc by NRG3EGF.Fc or NRG1EGF. Iodination of NRG3EGF.Fc and the binding assay were as described in Materials and Methods. ErbB4.Fc was immobilized on 96-well plates and incubated with various concentrations of unlabeled NRG3EGF.Fc or NRG1EGF and a constant amount of 125I-labeled NRG3EGF.Fc for 1.5 hr at room temperature. Unbound ligand was removed and the plate was extensively washed. The fraction of radioactivity bound over total 125I-NRG3EGF.Fc input is plotted against the concentration of competitor. Data of a representative experiment from four independent assays are shown. Error bars indicate standard deviation of quadruplicate samples of this experiment.