Figure 1. Architecture of the Kdp-ATPase.
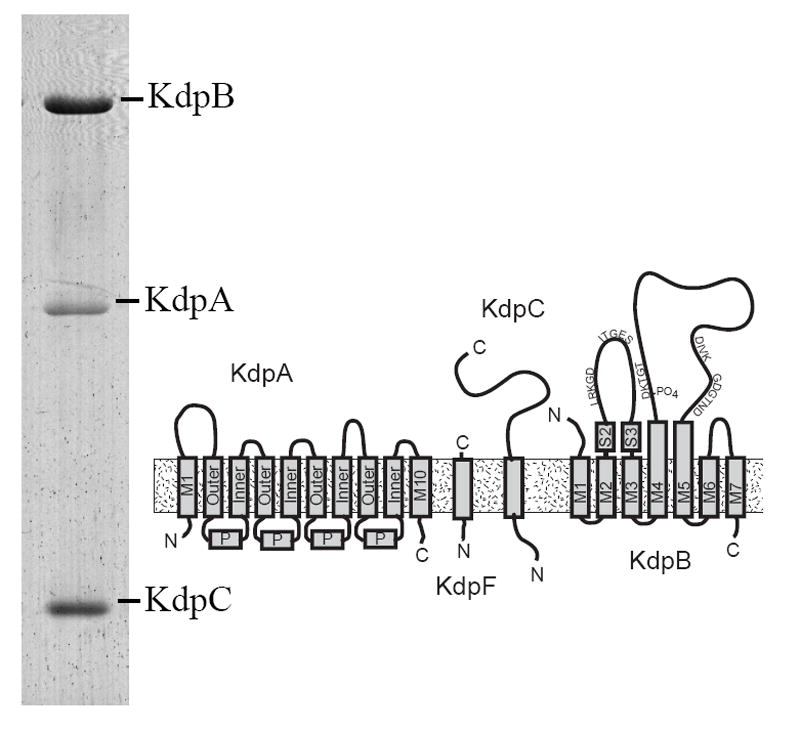
A Coomassie-stained SDS gel shows the preparation that was used for crystallization. Three of the four subunits are clearly resolved, whereas KdpF was too small (6.2 kD) to be retained by this gel system. KdpA is largely hydrophobic and is therefore more weakly stained than the other subunits. The diagram illustrates the topology of the four subunits composing the Kdp complex. KdpA consists of four repeats of the KcsA motif, labeled as “Outer”, “P” and “Inner”, with an additional helix at both the N- and C-termini. KdpB has seven transmembrane helices and sequence motifs conserved amongst all P-type ATPases along the cytoplasmic domains (indicated by the single letter amino acid code). KdpC and KdpF are smaller subunits with a single transmembrane helix.
