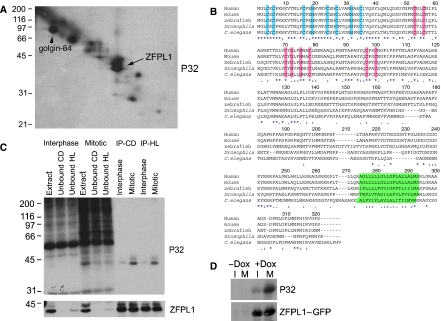
Figure 1.
Identification of ZFPL1 as a mitotic Golgi phosphoprotein. (A) Rat liver Golgi membranes were incubated with mitotic HeLa cytosol in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP and radiolabelled proteins analysed by 16-BAC/SDS–PAGE two-dimensional electrophoresis followed by autoradiography. The arrow indicates the position of the doublet identified as ZFPL1 by Q-TOF mass spectrometry. The position of the known phosphoprotein golgin-84 is also indicated. (B) Amino-acid sequence of human ZFPL1 (Acc. No. NP_006773) aligned with orthologues from mouse (Mus musculus, Acc. No. NP_077193), zebrafish (Danio rerio, Acc. No. NP_956967), Drosophila melanogaster (Acc. No. NP_732731) and Caenorhabditis elegans (Acc. No. NP_503731). Conserved residues in the N-terminus predicted to coordinate zinc within a novel type of zinc finger are in blue, whereas residues predicted to coordinate zinc within a ring finger are in pink. The predicted transmembrane domains are in green. Identical residues are indicated with an asterisk, whereas weakly and strongly similar residues are marked with one or two dots, respectively. (C) ZFPL1 was immunoprecipitated from denatured extracts prepared from Golgi membranes incubated with interphase or mitotic cytosol and [γ-32P]ATP. Total extracts, unbound fractions and proteins immunoprecipitated with antibodies to ZFPL1 cytoplasmic domain (CD) or hydrophilic region (HL) were analysed by SDS–PAGE followed by autoradiography (P32) and western blotting with antibodies to ZFPL1. (D) HEK293 cells stably expressing ZFPL1–GFP under the control of a Tet repressor were left uninduced (−Dox) or induced with doxycycline (+Dox) for 24 h in the absence (I) or presence of nocodazole (M) to enrich for mitotic cells. 32P-orthophosphate was included for the last 4 h and ZFPL1–GFP was immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibodies before analysis by autoradiography (P32) and western blotting with anti-ZFPL1 antibodies.