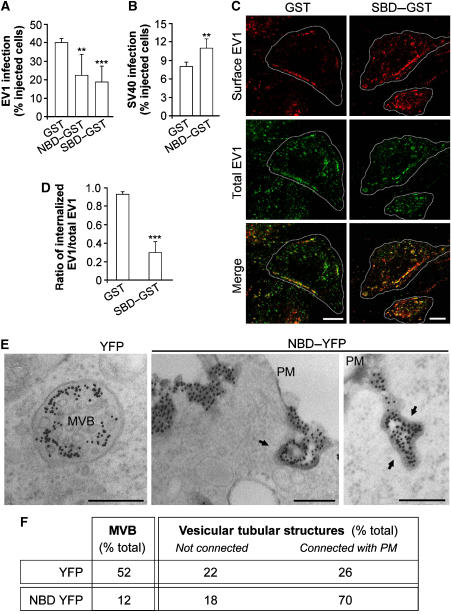
Figure 4.
Effects of CtBP1/BARS inhibition on infection and α2β1-mediated internalization of EV1 in SAOS cells. (A) Cells were microinjected with GST, NBD–GST or SBD–GST, as indicated, incubated with EV1 virus for 6 h and then fixed and quantified for EV1-infected cells (see Materials and methods). (B) As (A), with SV40 virus for 12 h, as indicated, for SV40-infected cells. (C) As (A), with EV1 virus for 2 h, as indicated. Cells were fixed and labelled for surface-bound (red) and total (green) EV1 (with non-permeabilized and permeabilized cells, respectively), with merged signal shown. Green dots in the merged signal represent internalized virus. (D) Quantification of the ratio of internalized to total EV1, as described in (C). More than 100 cells were analysed under each experimental condition, and the data are means±s.e. from three independent experiments. (E) Cells were transfected with empty YFP vector or NBD–YFP for 2 h, as indicated, then incubated for 2 h with an anti-α2-integrin antibody to induce integrin internalization and fixed and prepared for EM. Integrin was revealed with a gold-conjugated secondary antibody, and membranes accessible by extracellular medium were revealed by treatment with ruthenium red (electron-dense membranes). Left-hand panel, multivesicular body (MVB) in control cells. Centre and right-hand panels, integrin-labelled vesicular-tubular structures connected with the plasma membrane (PM). Arrows, electron-dense membranes. (F) Quantification from morphometric analysis of cells treated as in (E), showing per cent distributions of integrin-labelled membranes among the not connected/connected phenotypes, corrected for transfection efficiency (40%). Altogether 700 structures were counted under each condition. Scale bars: (C) 10 μm; (E) 200 nm. **P<0.005, ***P<0.001 (Student's t-test).