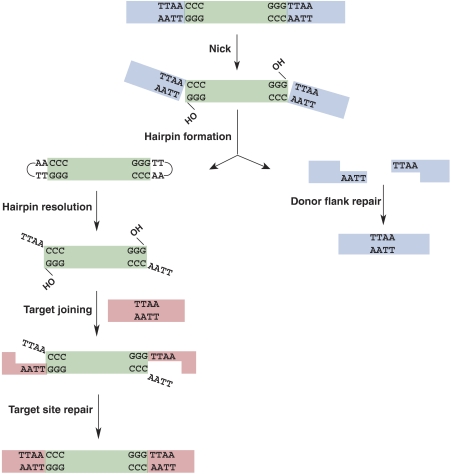
Figure 5.
Schematic representation of the piggyBac cut and paste transposition. piggyBac transposition initiates with nicks at the 3′ ends of the transposon, exposing 3′OHs. These 3′OHs then attack the complementary strand 4 nt into the flanking donor DNA, thereby forming hairpins on the transposon ends with the concomitant release of the transposon ends. Donor site repair can occur by ligation of the complementary 5′ TTAA overhangs on the flanking donor DNA ends, precisely reforming the TTAA target sequence. Transposon end hairpins are resolved by transposase, re-exposing the 3′OH transposon ends and generating 4 nt TTAA overhangs on the 5′ ends of the excised transposon. The 3′OH transposon ends join to the staggered positions at the 5′ T's of the TTAA/AATT target sequence. Repair of the single-strand gaps flanking the newly inserted transposon gives rise to the 4 bp TTAA target sequence duplication.