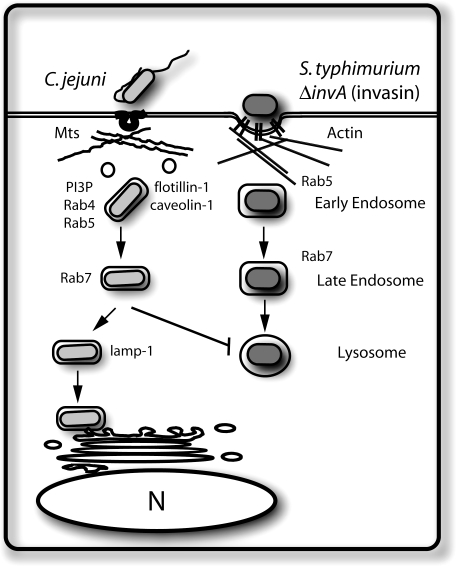
Figure 9. Model for C. jejuni Internalization and Trafficking within Epithelial Cells.
C. jejuni enters intestinal epithelial cell via a microtubule and caveolae-dependent process. After internalization, the C. jejuni–containing vacuole transiently acquires different markers of the endocytic pathway and ultimately survives within a compartment that is functionally separated from the canonical endocytic pathway, which is represented in this scheme by S. typhimurium invA (invasin).